Page 501 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 501
474 Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
The change of cross-section area is then
A 2
¼ð1 nεÞ (13.40)
A 0
and change of volume due to deformation is
V 2
¼ð1 nεÞ ð1 þ εÞ (13.41)
V 0
For liquids and rubber the volume is not changed during deformation, i.e., V/V 0 ¼ 1
(incompressible material) and n ¼ 0:5. For the majority of fiber-forming polymers
the volume is increased due to extension (i.e., V/V 0 > 1) and then n < 0:5 (obviously
0:2 n 0:45). In the case when volume is not changed during deformation the cross-
sectional area is reduced according to the following relation:
A l 0 1 2
¼ ¼ z ð1 0:5εÞ (13.42)
A 0 l 1 þ ε
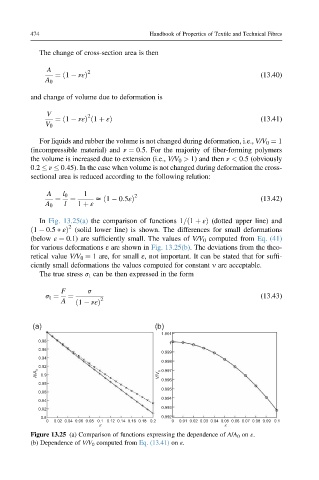
In Fig. 13.25(a) the comparison of functions 1=ð1 þ εÞ (dotted upper line) and
2
ð1 0:5 εÞ (solid lower line) is shown. The differences for small deformations
(below ε ¼ 0.1) are sufficiently small. The values of V/V 0 computed from Eq. (41)
for various deformations ε are shown in Fig. 13.25(b). The deviations from the theo-
retical value V/V 0 ¼ 1 are, for small ε, not important. It can be stated that for suffi-
ciently small deformations the values computed for constant n are acceptable.
The true stress s t can be then expressed in the form
F s
s t ¼ ¼ 2 (13.43)
A ð1 nεÞ
(a) (b)
1.001
0.98
1
0.96
0.999
0.94
0.998
0.92
A/A 0 0.9 V/V 0 0.997
0.996
0.88
0.995
0.86
0.994
0.84
0.82 0.993
0.8 0.992
0 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.1 0.12 0.14 0.16 0.18 0.2 0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.1
ε ε
Figure 13.25 (a) Comparison of functions expressing the dependence of A/A 0 on ε.
(b) Dependence of V/V 0 computed from Eq. (13.41) on ε.