Page 83 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 83
64 Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
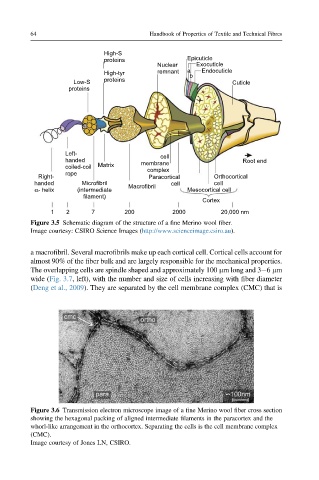
High-S
proteins Epicuticle
Nuclear Exocuticle
High-tyr remnant a b Endocuticle
proteins
Low-S Cuticle
proteins
Left- cell
handed membrane Root end
coiled-coil Matrix complex
rope
Right- Paracortical Orthocortical
handed Microfibril Macrofibril cell cell
α- helix (intermediate Mesocortical cell
filament)
Cortex
1 2 7 200 2000 20,000 nm
Figure 3.5 Schematic diagram of the structure of a fine Merino wool fiber.
Image courtesy: CSIRO Science Images (http://www.scienceimage.csiro.au).
a macrofibril. Several macrofibrils make up each cortical cell. Cortical cells account for
almost 90% of the fiber bulk and are largely responsible for the mechanical properties.
The overlapping cells are spindle shaped and approximately 100 mm long and 3e6 mm
wide (Fig. 3.7, left), with the number and size of cells increasing with fiber diameter
(Deng et al., 2009). They are separated by the cell membrane complex (CMC) that is
Figure 3.6 Transmission electron microscope image of a fine Merino wool fiber cross section
showing the hexagonal packing of aligned intermediate filaments in the paracortex and the
whorl-like arrangement in the orthocortex. Separating the cells is the cell membrane complex
(CMC).
Image courtesy of Jones LN, CSIRO.