Page 16 - Handbook of Surface Improvement and Modification
P. 16
2.1 Methods and mechanisms of protection 11
17
indenter. The fish-scale pattern is main-
tained until the ultimate strength of the
material is reached and material removal
17
begins. Materials having a high elastic
modulus resist indentation strains prior to
yielding and have shallower penetration
17
depths. The elastic modulus needs to be
balanced because high elastic modulus also
causes formation of stress concentrations
which can lead to cracking and crazing. 17
Surface friction is another important prop-
erty of material because low surface friction
reduces the tensile force acting on material
behind indenter, which reduces stick time
17
and suppresses scratch damage. Stress
whitening is caused by formation of numer-
ous small voids and crazes which cause
17
damage of optical properties. Polymers
having a high degree of crystallinity are
more resistant to this form of damage. 17
Nucleation of crystallization by filler parti-
cles (especially nanofillers) also reduces
stress whitening, providing that filler has
17
good adhesion to matrix polymer.
The introduction of surface texture
provides an additional means of control of
these interactions because the interface
between the scratch tip and surface is modi-
17
fied. Friction depends on contact area and
17
friction coefficient. The reduction of con-
tact area by surface texturing reduces fric-
17
tion. Proportion of size of scratch tip and
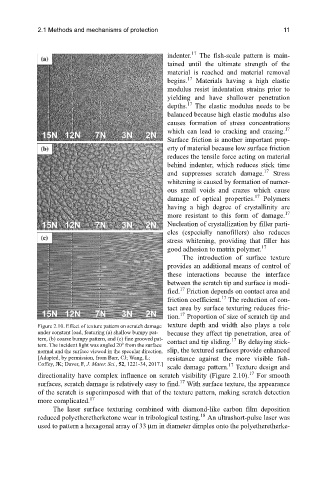
Figure 2.10. Effect of texture pattern on scratch damage texture depth and width also plays a role
under constant load, featuring (a) shallow bumpy pat- because they affect tip penetration, area of
tern, (b) coarse bumpy pattern, and (c) fine grooved pat- contact and tip sliding. By delaying stick-
17
o
tern. The incident light was angled 20 from the surface
normal and the surface viewed in the specular direction. slip, the textured surfaces provide enhanced
[Adapted, by permission, from Barr, CJ; Wang, L; resistance against the more visible fish-
Coffey, JK; Daver, F, J. Mater. Sci., 52, 1221-34, 2017.] 17
scale damage pattern. Texture design and
17
directionality have complex influence on scratch visibility (Figure 2.10). For smooth
17
surfaces, scratch damage is relatively easy to find. With surface texture, the appearance
of the scratch is superimposed with that of the texture pattern, making scratch detection
17
more complicated.
The laser surface texturing combined with diamond-like carbon film deposition
18
reduced polyetheretherketone wear in tribological testing. An ultrashort-pulse laser was
used to pattern a hexagonal array of 33 μm in diameter dimples onto the polyetheretherke-