Page 22 - Handbook of Surface Improvement and Modification
P. 22
2.2 Additives used 17
2.2.4 NANOCLAY
Photo-curable nanocomposites, based on 2,2-bis[4-(methacryloxypropoxy)-phenyl]pro-
pane) and tri(ethylene glycol)dimethacrylate) (50/50 wt%) were prepared using three
types of clay at different loading levels and evaluated for their application as hard and
30
anti-scratch coating material. Exfoliation or intercalation plays an important role, caus-
ing surface roughness, which affects adhesion by changing the characteristics of the coat-
30
ing-substrate interface. The highest scratch resistance was obtained for a sample
30
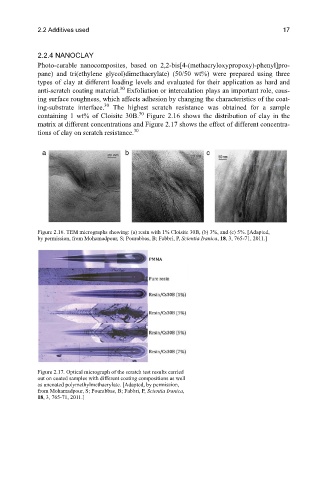
containing 1 wt% of Cloisite 30B. Figure 2.16 shows the distribution of clay in the
matrix at different concentrations and Figure 2.17 shows the effect of different concentra-
30
tions of clay on scratch resistance.
Figure 2.16. TEM micrographs showing: (a) resin with 1% Cloisite 30B, (b) 3%, and (c) 5%. [Adapted,
by permission, from Mohamadpour, S; Pourabbas, B; Fabbri, P, Scientia Iranica, 18, 3, 765-71, 2011.]
Figure 2.17. Optical micrograph of the scratch test results carried
out on coated samples with different coating compositions as well
as uncoated polymethylmethacrylate. [Adapted, by permission,
from Mohamadpour, S; Pourabbas, B; Fabbri, P, Scientia Iranica,
18, 3, 765-71, 2011.]