Page 277 - Hardware Implementation of Finite-Field Arithmetic
P. 277
m
Operations over GF (2 )—Normal Bases 257
A (m – 1: 0)
1 0 inic
NB_squaring
m-bit cyclic shift register shift_r
bb (m – 1: 0)
NB_multiplier
dd (m – 1: 0)
INV (m – 1 : 0)
inic
m-bit register
ce_c
cc (m – 1: 0)
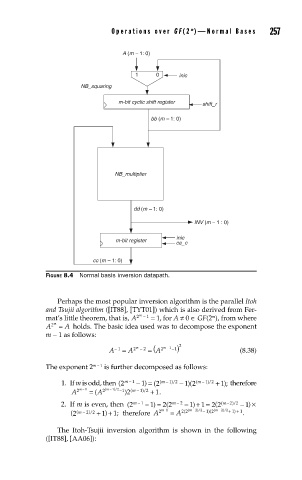
FIGURE 8.4 Normal basis inversion datapath.
Perhaps the most popular inversion algorithm is the parallel Itoh
and Tsujii algorithm ([IT88], [TYT01]) which is also derived from Fer-
m
m
mat’s little theorem, that is, A 2 − 1 = 1, for A ≠ 0 ∈ GF(2 ), from where
A 2 m = A holds. The basic idea used was to decompose the exponent
m − 1 as follows:
− 1 2 m − 2 A ( 2 m − 1 − ) 2
1
A = A = (8.38)
The exponent 2 m − 1 is further decomposed as follows:
)/
)/
) (2
1. If m is odd, then (2 m − 1 − 1 = (m − 12 − 1 )(2 (m − 12 + 1 ); therefore
−
−
−
)
/
)
/
A 2 m 1 = ( A 2 ( m 1 2 − 1 2 ) ( m 1 2 + 1.
)/
2. If m is even, then (2 m − 1 − ) 1 = ( 2 2 m − 2 − ) 1 + = ( 2 2 (m− 22 − ) 1 ×
1
−
−
−
/
)
)
/
)
(
)
(
)/
(2 (m − 22 + ) 1 + ; 1 therefore A 2 m 1 = A 2 2 ( m 2 2 − 1 2 ( m 2 2 + 1 + 1 .
The Itoh-Tsujii inversion algorithm is shown in the following
([IT88], [AA06]):