Page 67 - Hardware Implementation of Finite-Field Arithmetic
P. 67
50 Cha pte r T w o
x (11..8) & x′ (9..8) & 0 &
x (11..8) x (7..0) 0 & x′ (9..8) x′ (7..0)
0 0 000 0
9-bit adder 9-bit adder
x (15..12) & 0 & x′′ (8..0) –239(273)
x (15..12) 0
x′′ (7..0)
0 0
10-bit adder
10-bit adder
dif (9) dif
x′ (9..0)
dif (7..0)
0 1
x mod 239
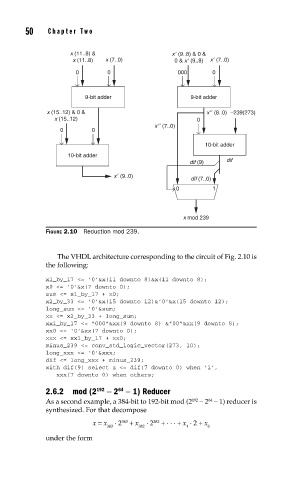
FIGURE 2.10 Reduction mod 239.
The VHDL architecture corresponding to the circuit of Fig. 2.10 is
the following:
x1_by_17 <= ‘0’&x(11 downto 8)&x(11 downto 8);
x0 <= ‘0’&x(7 downto 0);
sum <= x1_by_17 + x0;
x2_by_33 <= ‘0’&x(15 downto 12)&’0’&x(15 downto 12);
long_sum <= ‘0’∑
xx <= x2_by_33 + long_sum;
xx1_by_17 <= “000”&xx(9 downto 8) &”00”&xx(9 downto 8);
xx0 <= ‘0’&xx(7 downto 0);
xxx <= xx1_by_17 + xx0;
minus_239 <= conv_std_logic_vector(273, 10);
long_xxx <= ‘0’&xxx;
dif <= long_xxx + minus_239;
with dif(9) select z <= dif(7 downto 0) when ‘1’,
xxx(7 downto 0) when others;
64
192
2.6.2 mod (2 − 2 − 1) Reducer
64
192
As a second example, a 384-bit to 192-bit mod (2 − 2 − 1) reducer is
synthesized. For that decompose
382
x = x · 2 + x · 2 + . . . + x · 2 + x
383
383 382 1 0
under the form