Page 234 - High Power Laser Handbook
P. 234
202 So l i d - S t at e La s e r s Zigzag Slab Lasers 203
Piston sensor
Master YDFA Frequency-shifted reference beam
oscillator AOM
Power amplifier chains
PM YDFA PA
Tiled, high-power
output beam
Adaptive
optics
Wavefront
sensors
Phase control
electronics
Heterodyne detectors
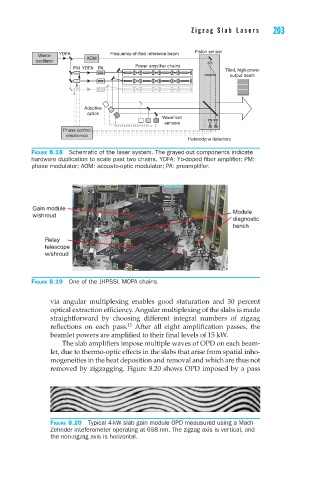
Figure 8.18 Schematic of the laser system. The grayed-out components indicate
hardware duplication to scale past two chains. YDFA: Yb-doped fiber amplifier; PM:
phase modulator; AOM: acousto-optic modulator; PA: preamplifier.
Gain module
w/shroud Module
diagnostic
bench
Relay
telescope
w/shroud
Figure 8.19 One of the JHPSSL MOPA chains.
via angular multiplexing enables good staturation and 30 percent
optical extraction efficiency. Angular multiplexing of the slabs is made
straightforward by choosing different integral numbers of zigzag
15
reflections on each pass. After all eight amplification passes, the
beamlet powers are amplified to their final levels of 15 kW.
The slab amplifiers impose multiple waves of OPD on each beam-
let, due to thermo-optic effects in the slabs that arise from spatial inho-
mogeneities in the heat deposition and removal and which are thus not
removed by zigzagging. Figure 8.20 shows OPD imposed by a pass
Figure 8.20 Typical 4-kW slab gain module OPD meausured using a Mach-
Zehnder inteferometer operating at 658 nm. The zigzag axis is vertical, and
the non-zigzag axis is horizontal.