Page 231 - High Power Laser Handbook
P. 231
200 So l i d - S t at e La s e r s Zigzag Slab Lasers 201
coupled through the slab edges so that it propagates and is
absorbed along the non-zigzag slab axis. Such an architecture pro-
vides more surface area for pump injection and reduces pump
brightness requirements. However, a significant challenge with
edge-pumped slabs that is not present in end-pumped slabs is
OPD along the non-zigzag axis, which is driven by exponential
(Beer’s law) absorption of pump light.
8.4.2 Performance
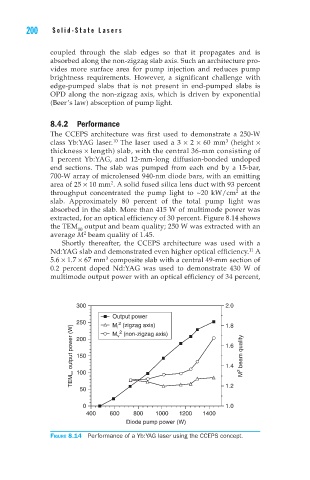
The CCEPS architecture was first used to demonstrate a 250-W
10
3
class Yb:YAG laser. The laser used a 3 × 2 × 60 mm (height ×
thickness × length) slab, with the central 36-mm consisting of
1 percent Yb:YAG, and 12-mm-long diffusion-bonded undoped
end sections. The slab was pumped from each end by a 15-bar,
700-W array of microlensed 940-nm diode bars, with an emitting
area of 25 × 10 mm . A solid fused silica lens duct with 93 percent
2
2
throughput concentrated the pump light to ~20 kW/cm at the
slab. Approximately 80 percent of the total pump light was
absorbed in the slab. More than 415 W of multimode power was
extracted, for an optical efficiency of 30 percent. Figure 8.14 shows
the TEM output and beam quality; 250 W was extracted with an
00
average M beam quality of 1.45.
2
Shortly thereafter, the CCEPS architecture was used with a
11
Nd:YAG slab and demonstrated even higher optical efficiency. A
3
5.6 × 1.7 × 67 mm composite slab with a central 49-mm section of
0.2 percent doped Nd:YAG was used to demonstrate 430 W of
multimode output power with an optical efficiency of 34 percent,
300 2.0
Output power
250 M (zigzag axis) 1.8
2
TEM ∞ output power (W) 150 1.6 M 2 beam quality
I
2
(non-zigzag axis)
M v
200
1.4
100
50 1.2
0 1.0
400 600 800 1000 1200 1400
Diode pump power (W)
Figure 8.14 Performance of a Yb:YAG laser using the CCEPS concept.