Page 229 - High Power Laser Handbook
P. 229
198 So l i d - S t at e La s e r s Zigzag Slab Lasers 199
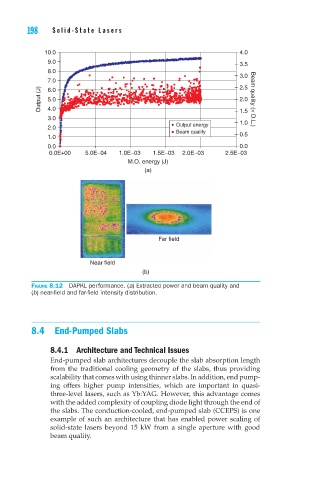
10.0 4.0
9.0 3.5
8.0
3.0
7.0 2.5
6.0
Output (J) 5.0 2.0 Beam quality (× D.L.)
4.0
3.0 1.5
1.0
2.0 Output energy
Beam quality 0.5
1.0
0.0 0.0
0.0E+00 5.0E−04 1.0E−03 1.5E−03 2.0E−03 2.5E−03
M.O. energy (J)
(a)
Far field
Near field
(b)
Figure 8.12 DAPKL performance. (a) Extracted power and beam quality and
(b) near-field and far-field intensity distribution.
8.4 End-Pumped Slabs
8.4.1 Architecture and Technical Issues
End-pumped slab architectures decouple the slab absorption length
from the traditional cooling geometry of the slabs, thus providing
scalability that comes with using thinner slabs. In addition, end pump-
ing offers higher pump intensities, which are important in quasi-
three-level lasers, such as Yb:YAG. However, this advantage comes
with the added complexity of coupling diode light through the end of
the slabs. The conduction-cooled, end-pumped slab (CCEPS) is one
example of such an architecture that has enabled power scaling of
solid-state lasers beyond 15 kW from a single aperture with good
beam quality.