Page 361 - High Power Laser Handbook
P. 361
330 So l i d - S t at e La s e r s Ultrafast Lasers in Thin-Disk Geometry 331
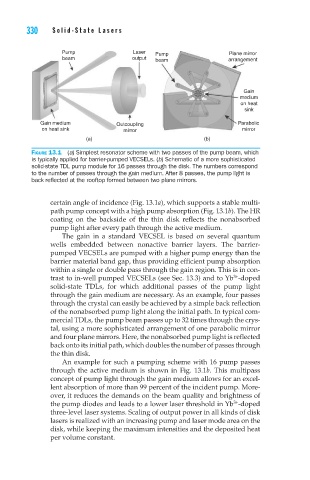
Pump Laser Pump Plane mirror
beam output beam arrangement
Gain
medium
on heat
sink
Gain medium Outcoupling Parabolic
on heat sink mirror mirror
(a) (b)
Figure 13.1 (a) Simplest resonator scheme with two passes of the pump beam, which
is typically applied for barrier-pumped VECSELs. (b) Schematic of a more sophisticated
solid-state TDL pump module for 16 passes through the disk. The numbers correspond
to the number of passes through the gain medium. After 8 passes, the pump light is
back reflected at the rooftop formed between two plane mirrors.
certain angle of incidence (Fig. 13.1a), which supports a stable multi-
path pump concept with a high pump absorption (Fig. 13.1b). The HR
coating on the backside of the thin disk reflects the nonabsorbed
pump light after every path through the active medium.
The gain in a standard VECSEL is based on several quantum
wells embedded between nonactive barrier layers. The barrier-
pumped VECSELs are pumped with a higher pump energy than the
barrier material band gap, thus providing efficient pump absorption
within a single or double pass through the gain region. This is in con-
3+
trast to in-well pumped VECSELs (see Sec. 13.3) and to Yb -doped
solid-state TDLs, for which additional passes of the pump light
through the gain medium are necessary. As an example, four passes
through the crystal can easily be achieved by a simple back reflection
of the nonabsorbed pump light along the initial path. In typical com-
mercial TDLs, the pump beam passes up to 32 times through the crys-
tal, using a more sophisticated arrangement of one parabolic mirror
and four plane mirrors. Here, the nonabsorbed pump light is reflected
back onto its initial path, which doubles the number of passes through
the thin disk.
An example for such a pumping scheme with 16 pump passes
through the active medium is shown in Fig. 13.1b. This multipass
concept of pump light through the gain medium allows for an excel-
lent absorption of more than 99 percent of the incident pump. More-
over, it reduces the demands on the beam quality and brightness of
3+
the pump diodes and leads to a lower laser threshold in Yb -doped
three-level laser systems. Scaling of output power in all kinds of disk
lasers is realized with an increasing pump and laser mode area on the
disk, while keeping the maximum intensities and the deposited heat
per volume constant.