Page 180 - High Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Fundamentals, Design and Applications
P. 180
Anodes 157
q I mV vs. RHE
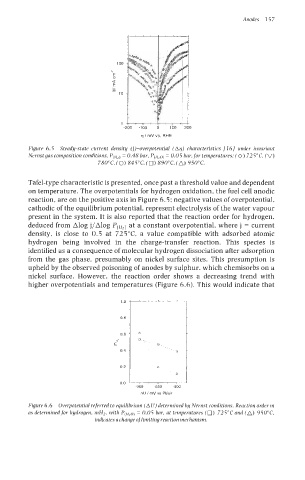
Figure 6.5 Steady-state current density (j)-overpotential (Aq) characteristics 11 61 under invariant
Nernst gas composition conditions, P(H2) = 0.48 bar, P(,,o) = 0.05 bar,for temperatures: (0) 725°C (V)
780"C, (0) 845"C, (0) 890"C, (A) 950°C.
Tafel-type characteristic is presented, once past a threshold value and dependent
on temperature. The overpotentials for hydrogen oxidation, the fuel cell anodic
reaction, are on the positive axis in Figure 6.5; negative values of overpotential,
cathodic of the equilibrium potential, represent electrolysis of the water vapour
present in the system. It is also reported that the reaction order for hydrogen,
deduced from Alog j/Alog P(Hr) at a constant overpotential, where j = current
density, is close to 0.5 at 725°C a value compatible with adsorbed atomic
hydrogen being involved in the charge-transfer reaction. This species is
identified as a consequence of molecular hydrogen dissociation after adsorption
from the gas phase, presumably on nickel surface sites. This presumption is
upheld by the observed poisoning of anodes by sulphur, which chemisorbs on a
nickel surface. However, the reaction order shows a decreasing trend with
higher overpotentials and temperatures (Figure 6.6). This would indicate that
0.6 -
0.6 -
E
0.4 -
0.2
0.0
-900 -850 -600
AU I rnV vs PtJair
Figure 6.6 Overpotential referred to equilibrium (AU) determined by Nernst conditions. Reaction order m
as determinedfor hydrogen, mH2, with P(H>o) = 0.05 bar, at temperatures (0) 725°C and (A) 950°C.
indicates a change oflimiting reaction mechanism.