Page 71 - How To Implement Lean Manufacturing
P. 71
52 Cha pte r T h ree
Second, kanban creates an absolute limit on total inventory. Since each kanban rep-
resents a certain amount of stock, and the number of kanban are strictly controlled and
limited, this creates an upper limit on the inventory. We will show in Chap. 4 that this
inventory limitation is a key factor in making a pull production system function. By
utilizing pull production, we minimize overproduction. Furthermore, the continuous
improvement aspect of kanban works to further reduce this overproduction.
What Is Value Added Time?
Total time—all the time it takes to produce the product, which is made up of:
• Value added time—the time the customer is willing to pay for
• Non-value added time—which is waste. It is comprised of:
• Pure waste—Activities that can be eliminated or reduced immediately.
• Necessary waste—Activities that cannot be reduced immediately due to
the present work rules or technology.
Finished Goods Inventory Calculations
Cycle Stock Calculation
Cycle stock, you will recall, is the stock that is the volume you need on hand to take care
of the normal demand pickups by your customer. Hence, we will calculate the cycle
stock volume to be the production rate multiplied by the replenishment time plus some
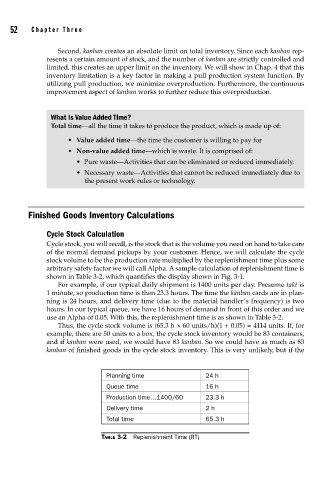
arbitrary safety factor we will call Alpha. A sample calculation of replenishment time is
shown in Table 3-2, which quantifies the display shown in Fig. 3-1.
For example, if our typical daily shipment is 1400 units per day. Presume takt is
1 minute, so production time is then 23.3 hours. The time the kanban cards are in plan-
ning is 24 hours, and delivery time (due to the material handler’s frequency) is two
hours. In our typical queue, we have 16 hours of demand in front of this order and we
use an Alpha of 0.05. With this, the replenishment time is as shown in Table 3-2.
Thus, the cycle stock volume is (65.3 h × 60 units/h)(1 + 0.05) = 4114 units. If, for
example, there are 50 units to a box, the cycle stock inventory would be 83 containers,
and if kanban were used, we would have 83 kanban. So we could have as much as 83
kanban of finished goods in the cycle stock inventory. This is very unlikely, but if the
Planning time 24 h
Queue time 16 h
Production time…1400/60 23.3 h
Delivery time 2 h
Total time 65.3 h
TABLE 3-2 Replenishment Time (RT)