Page 195 - How To Solve Word Problems In Calculus
P. 195
P1: FYN/FZQ P2: FXS
PB056-07 Macros-FMT June 1, 2001 13:49 Char Count= 0
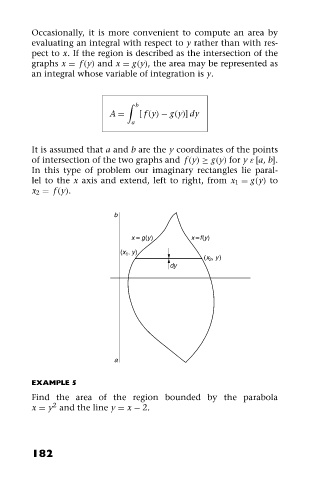
Occasionally, it is more convenient to compute an area by
evaluating an integral with respect to y rather than with res-
pect to x. If the region is described as the intersection of the
graphs x = f (y) and x = g(y), the area may be represented as
an integral whose variable of integration is y.
b
A = [ f (y) − g(y)] dy
a
It is assumed that a and b are the y coordinates of the points
of intersection of the two graphs and f (y) ≥ g(y) for y ε [a, b].
In this type of problem our imaginary rectangles lie paral-
lel to the x axis and extend, left to right, from x 1 = g(y)to
x 2 = f (y).
b
x = g(y) x = f(y)
, y)
(x 1
, y)
(x 2
dy
a
EXAMPLE 5
Find the area of the region bounded by the parabola
2
x = y and the line y = x − 2.
182