Page 184 - Human Inspired Dexterity in Robotic Manipulation
P. 184
182 Human Inspired Dexterity in Robotic Manipulation
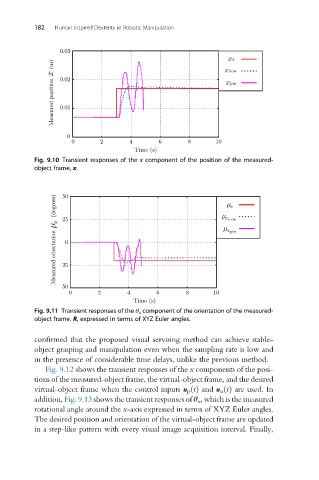
0.03
xd
Measured position x (m) 0.02 xpre
xnew
0.01
0
0 2 4 6 8 10
Time (s)
Fig. 9.10 Transient responses of the x component of the position of the measured-
object frame, x.
Measured orientation µ x (degrees) 25 0 µ x new
50
µ x
µ x pre
–25
–50
0 2 4 6 8 10
Time (s)
Fig. 9.11 Transient responses of the θ x component of the orientation of the measured-
object frame, R, expressed in terms of XYZ Euler angles.
confirmed that the proposed visual servoing method can achieve stable-
object grasping and manipulation even when the sampling rate is low and
in the presence of considerable time delays, unlike the previous method.
Fig. 9.12 shows the transient responses of the x components of the posi-
tions of the measured-object frame, the virtual-object frame, and the desired
virtual-object frame when the control inputs u p tðÞ and u o tðÞ are used. In
addition, Fig. 9.13 shows the transient responses of θ x , which is the measured
rotational angle around the x-axis expressed in terms of XYZ Euler angles.
The desired position and orientation of the virtual-object frame are updated
in a step-like pattern with every visual image acquisition interval. Finally,