Page 118 - Hybrid-Renewable Energy Systems in Microgrids
P. 118
102 Hybrid-Renewable Energy Systems in Microgrids
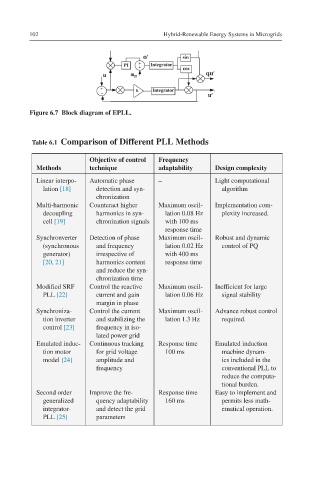
Figure 6.7 Block diagram of EPLL.
Table 6.1 Comparison of Different PLL Methods
Objective of control Frequency
Methods technique adaptability Design complexity
Linear interpo- Automatic phase – Light computational
lation [18] detection and syn- algorithm
chronization
Multi-harmonic Counteract higher Maximum oscil- Implementation com-
decoupling harmonics in syn- lation 0.08 Hz plexity increased.
cell [19] chronization signals with 100 ms
response time
Synchronverter Detection of phase Maximum oscil- Robust and dynamic
(synchronous and frequency lation 0.02 Hz control of PQ
generator) irrespective of with 400 ms
[20, 21] harmonics content response time
and reduce the syn-
chronization time
Modified SRF Control the reactive Maximum oscil- Inefficient for large
PLL [22] current and gain lation 0.06 Hz signal stability
margin in phase
Synchroniza- Control the current Maximum oscil- Advance robust control
tion inverter and stabilizing the lation 1.3 Hz required.
control [23] frequency in iso-
lated power grid
Emulated induc- Continuous tracking Response time Emulated induction
tion motor for grid voltage 100 ms machine dynam-
model [24] amplitude and ics included in the
frequency conventional PLL to
reduce the computa-
tional burden.
Second order Improve the fre- Response time Easy to implement and
generalized quency adaptability 160 ms permits less math-
integrator- and detect the grid ematical operation.
PLL [25] parameters