Page 47 - Hydrocarbon
P. 47
34 Exploration Methods and Techniques
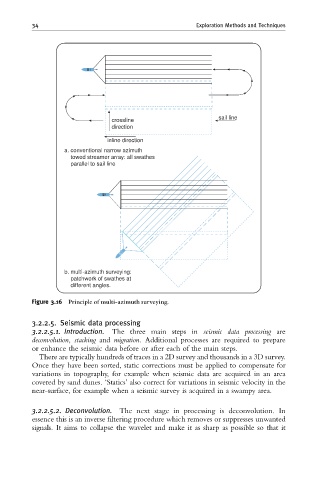
sail line
crossline
direction
inline direction
a. conventional narrow azimuth
towed streamer array: all swathes
parallel to sail line
b. multi-azimuth surveying:
patchwork of swathes at
different angles.
Figure 3.16 Principle of multi-azimuth surveying.
3.2.2.5. Seismic data processing
3.2.2.5.1. Introduction. The three main steps in seismic data processing are
deconvolution, stacking and migration. Additional processes are required to prepare
or enhance the seismic data before or after each of the main steps.
There are typically hundreds of traces in a 2D survey and thousands in a 3D survey.
Once they have been sorted, static corrections must be applied to compensate for
variations in topography, for example when seismic data are acquired in an area
covered by sand dunes. ‘Statics’ also correct for variations in seismic velocity in the
near-surface, for example when a seismic survey is acquired in a swampy area.
3.2.2.5.2. Deconvolution. The next stage in processing is deconvolution. In
essence this is an inverse filtering procedure which removes or suppresses unwanted
signals. It aims to collapse the wavelet and make it as sharp as possible so that it