Page 123 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 123
110 Reservoir Fluids
H H H H H H H
H C C C H H C C C C H
H H H H H
H C H H C H
H H
iso-butane iso-pentane
(i-C H ) (i-C H )
4 10
5 12
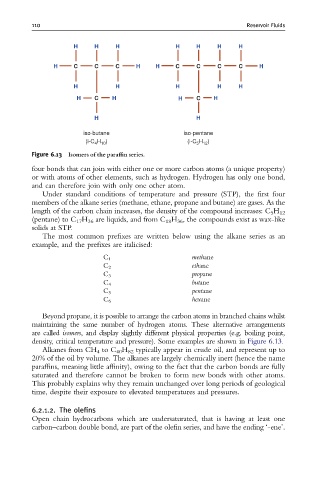
Figure 6.13 Isomers of the para⁄n series.
four bonds that can join with either one or more carbon atoms (a unique property)
or with atoms of other elements, such as hydrogen. Hydrogen has only one bond,
and can therefore join with only one other atom.
Under standard conditions of temperature and pressure (STP), the first four
members of the alkane series (methane, ethane, propane and butane) are gases. As the
length of the carbon chain increases, the density of the compound increases: C 5 H 12
(pentane) to C 17 H 36 are liquids, and from C 18 H 36 , the compounds exist as wax-like
solids at STP.
The most common prefixes are written below using the alkane series as an
example, and the prefixes are italicised:
methane
C 1
ethane
C 2
C 3 propane
C 4 butane
pentane
C 5
hexane
C 6
Beyond propane, it is possible to arrange the carbon atoms in branched chains whilst
maintaining the same number of hydrogen atoms. These alternative arrangements
are called isomers, and display slightly different physical properties (e.g. boiling point,
density, critical temperature and pressure). Some examples are shown in Figure 6.13.
Alkanes from CH 4 to C 40 H 82 typically appear in crude oil, and represent up to
20% of the oil by volume. The alkanes are largely chemically inert (hence the name
paraffins, meaning little affinity), owing to the fact that the carbon bonds are fully
saturated and therefore cannot be broken to form new bonds with other atoms.
This probably explains why they remain unchanged over long periods of geological
time, despite their exposure to elevated temperatures and pressures.
6.2.1.2. The olefins
Open chain hydrocarbons which are undersaturated, that is having at least one
carbon–carbon double bond, are part of the olefin series, and have the ending ‘-ene’.