Page 127 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 127
114 Reservoir Fluids
gas
room Alkanes C − C 4
1
temp.
Alkanes C +
8
petrol 30-65°C
Alkanes C - C 8 Aromatics Benzene,
5
65-200°C Naphtha Methylbenzene (Toluene)
Complex Alkanes Dimethylbenzene (Xylenes)
Aromatics 175-275°C Naphthenes
e g. Naphthalene, Cyclopentane,Cyclohexane
Anthracene,
Naphthenes 275-400°C
Complex Alkanes
Alkanes Aromatics
(long chains & >400°C
branched chains) Mixed types
Aromatics
Mixed Types
residue
bitumen
heated crude oil
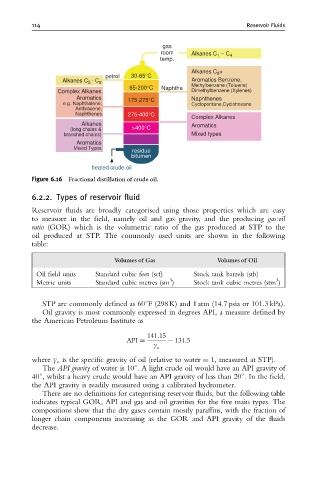
Figure 6.16 Fractional distillation of crude oil.
6.2.2. Types of reservoir fluid
Reservoir fluids are broadly categorised using those properties which are easy
to measure in the field, namely oil and gas gravity, and the producing gas:oil
ratio (GOR) which is the volumetric ratio of the gas produced at STP to the
oil produced at STP. The commonly used units are shown in the following
table:
Volumes of Gas Volumes of Oil
Oil field units Standard cubic feet (scf) Stock tank barrels (stb)
3 3
Metric units Standard cubic metres (sm ) Stock tank cubic metres (stm )
STP are commonly defined as 601F (298 K) and 1 atm (14.7 psia or 101.3 kPa).
Oil gravity is most commonly expressed in degrees API, a measure defined by
the American Petroleum Institute as
141:15
API ¼ 131:5
g o
where g o is the specific gravity of oil (relative to water ¼ 1, measured at STP).
The API gravity of water is 101. A light crude oil would have an API gravity of
401, whilst a heavy crude would have an API gravity of less than 201. In the field,
the API gravity is readily measured using a calibrated hydrometer.
There are no definitions for categorising reservoir fluids, but the following table
indicates typical GOR, API and gas and oil gravities for the five main types. The
compositions show that the dry gases contain mostly paraffins, with the fraction of
longer chain components increasing as the GOR and API gravity of the fluids
decrease.