Page 203 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 203
HYDC05 12/5/05 5:35 PM Page 186
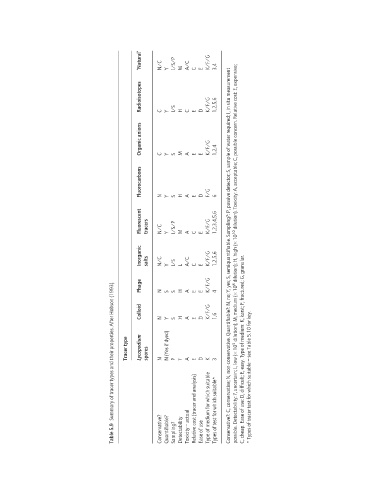
‘Natural’ N/C Y I/S/P M A/C C E K/F/G 3,4
Radioisotopes C Y I/S H C E D K/F/G 1,2,5,6
Organic anions C Y S M A E E K/F/G 1,2,4
Fluorocarbons N Y S H A E D F/G 6
Fluorescent tracers N/C Y I/S/P M A C E K/F/G 1,2,3,4,5,6
Inorganic salts N/C Y I/S L A/C C E K/F/G 1,2,5,6 Conservative?: C, conservative; N, non-conservative. Quantifiable?: N, no; Y, yes; S, semiquantifiable. Sampling?: P, passive detector; S, sample of water required; I, in situ measurement possible. Detectability: ?, uncertain; L, low (× 10 5 dilution); M, medium (× 10 8 dilution); H, high (× 10 10 dilution). Toxicity: A, acceptable; C, possible concern. Relative cost:
Phage N S S H A E E K/F/G 4
Summary of tracer types and their properties. After Hobson (1993).
Colloid N Y S H A E D K/F/G 1,6
Tracer type Lycopodium spores N N (Yes if dyed) P ? A E D K 3 C, cheap. Ease of use: D, difficult; E, easy. Type of medium: K, karst; F, fractured; G, granular. * Types of tracer test for which suitable – see Table 5.10 for key.
Relative cost (tracer and analysis) Type of medium for which suitable Types of test for which suitable*
Table 5.9 Conservative? Quantifiable? Sampling? Detectability Toxicity – actual Ease of use