Page 211 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 211
HYDC05 12/5/05 5:35 PM Page 194
194 Chapter Five
BO X
Groundwater modelling of the Monturaqui-Negrillar-Tilopozo aquifer, Chile
5.6
The Monturaqui-Negrillar-Tilopozo (MNT) aquifer is located at the As part of a sustainability assessment of the region, it has been
foot of the Andes in the extremely arid environment of northern suggested that a decline in water level of approximately 0.25 m,
Chile and occupies a north–south oriented graben approxim- equivalent to a reduction in aquifer outflow of approximately 6%,
ately 60 km long, with surface elevations decreasing from around should not be exceeded in order to protect the flora and fauna of
3200 m in the southern (Monturaqui) area to 2300 m in the north the Tilopozo wetland. The MNT aquifer and the established
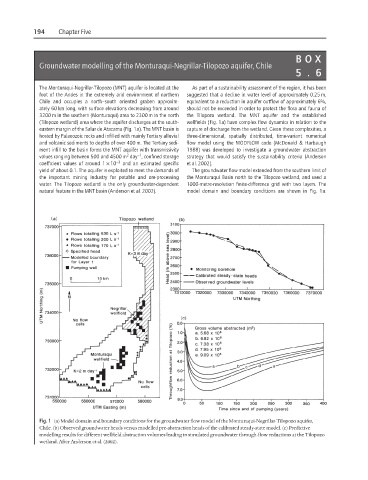
(Tilopozo wetland) area where the aquifer discharges at the south- wellfields (Fig. 1a) have complex flow dynamics in relation to the
eastern margin of the Salar de Atacama (Fig. 1a). The MNT basin is capture of discharge from the wetland. Given these complexities, a
hosted by Palaeozoic rocks and infilled with mainly Tertiary alluvial three-dimensional, spatially distributed, time-variant numerical
and volcanic sediments to depths of over 400 m. The Tertiary sedi- flow model using the MODFLOW code (McDonald & Harbaugh
ment infill to the basin forms the MNT aquifer with transmissivity 1988) was developed to investigate a groundwater abstraction
2
−1
values ranging between 500 and 4500 m day , confined storage strategy that would satisfy the sustainability criteria (Anderson
coefficient values of around 1 × 10 −3 and an estimated specific et al. 2002).
yield of about 0.1. The aquifer is exploited to meet the demands of The groundwater flow model extended from the southern limit of
the important mining industry for potable and ore-processing the Monturaqui Basin north to the Tilopozo wetland, and used a
water. The Tilopozo wetland is the only groundwater-dependent 1000-metre-resolution finite-difference grid with two layers. The
natural feature in the MNT basin (Anderson et al. 2002). model domain and boundary conditions are shown in Fig. 1a.
Fig. 1 (a) Model domain and boundary conditions for the groundwater flow model of the Monturaqui-Negrillar-Tilopozo aquifer,
Chile. (b) Observed groundwater heads versus modelled pre-abstraction heads of the calibrated steady-state model. (c) Predictive
modelling results for different wellfield abstraction volumes leading to simulated groundwater through-flow reductions at the Tilopozo
wetland. After Anderson et al. (2002).