Page 285 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 285
HYDC07 12/5/05 5:33 PM Page 268
268 Chapter Seven
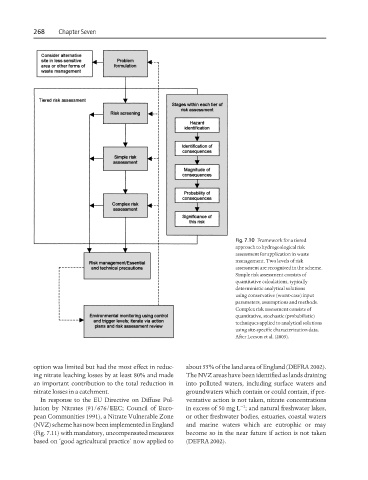
Fig. 7.10 Framework for a tiered
approach to hydrogeological risk
assessment for application in waste
management. Two levels of risk
assessment are recognized in the scheme.
Simple risk assessment consists of
quantitative calculations, typically
deterministic analytical solutions
using conservative (worst-case) input
parameters, assumptions and methods.
Complex risk assessment consists of
quantitative, stochastic (probabilistic)
techniques applied to analytical solutions
using site-specific characterization data.
After Leeson et al. (2003).
option was limited but had the most effect in reduc- about 55% of the land area of England (DEFRA 2002).
ing nitrate leaching losses by at least 80% and made The NVZ areas have been identified as lands draining
an important contribution to the total reduction in into polluted waters, including surface waters and
nitrate losses in a catchment. groundwaters which contain or could contain, if pre-
In response to the EU Directive on Diffuse Pol- ventative action is not taken, nitrate concentrations
−1
lution by Nitrates (91/676/EEC; Council of Euro- in excess of 50 mg L ; and natural freshwater lakes,
pean Communities 1991), a Nitrate Vulnerable Zone or other freshwater bodies, estuaries, coastal waters
(NVZ) scheme has now been implemented in England and marine waters which are eutrophic or may
(Fig. 7.11) with mandatory, uncompensated measures become so in the near future if action is not taken
based on ‘good agricultural practice’ now applied to (DEFRA 2002).