Page 305 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 305
HYDC08 12/5/05 5:31 PM Page 288
288 Chapter Eight
Cryptosporidium). Current efforts to address the regu- known. Flow conditions during riverbank filtration
lation of riverbank filtration focus on the removal are commonly described using interpretations of water-
of microbial pathogens and are contained in the level measurements and hydrogeological modelling.
Proposed Long Term 2 Enhanced Surface Water An important factor is the formation of the colmation
Treatment Rule (LT2ESWTR) of the United States layer at the interface between surface water and
Environmental Protection Agency (2001). groundwater. This layer has a reduced hydraulic con-
Riverbank filtration can occur under natural con- ductivity due to clogging from the input and pre-
ditions or be induced by lowering the groundwater cipitation of sediment particles, micro-organisms and
table below the surface water level by abstraction colloids, precipitation of iron and manganese oxy-
from adjacent boreholes. Typical flow conditions hydroxides and calcium carbonates as well as gas bub-
associated with different types of riverbank filtration bles. Schubert (2002) reported that the permeability
schemes are shown in Fig. 8.6. For the quantitative of clogged areas varies with the dynamic hydrology
and qualitative management of riverbank filtration and cannot be regarded as constant, particularly fol-
systems, the catchment zones, infiltration zones, mix- lowing periods of flooding. The hydraulic conductiv-
ing proportions in the pumped raw water, flowpaths ity of the river bed is therefore a principal factor
and flow velocities of the bank filtrate need to be determining the volume of bank filtrate.
BO X
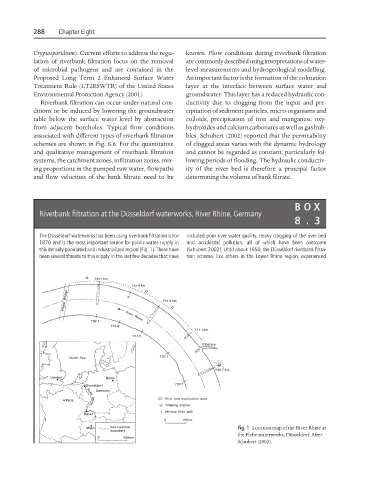
Riverbank filtration at the Düsseldorf waterworks, River Rhine, Germany
8.3
The Düsseldorf waterworks has been using riverbank filtration since included poor river water quality, heavy clogging of the river bed
1870 and is the most important source for public water supply in and accidental pollution, all of which have been overcome
this densely populated and industrialized region (Fig. 1). There have (Schubert 2002). Until about 1950, the Düsseldorf riverbank filtra-
been several threats to this supply in the last few decades that have tion scheme, like others in the Lower Rhine region, experienced
Fig. 1 Location map of the River Rhine at
the Flehe waterworks, Düsseldorf. After
Schubert (2002).