Page 306 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 306
HYDC08 12/5/05 5:31 PM Page 289
Groundwater resources and environmental management 289
BO X
Continued
8.3
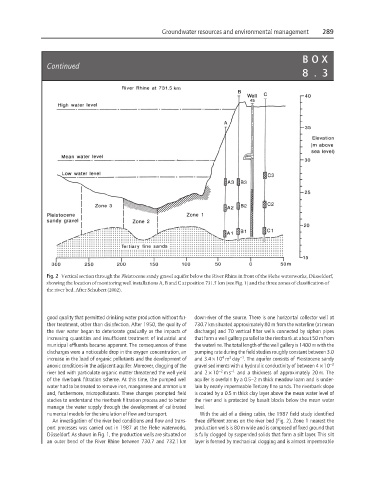
Fig. 2 Vertical section through the Pleistocene sandy gravel aquifer below the River Rhine in front of the Flehe waterworks, Düsseldorf,
showing the location of monitoring well installations A, B and C at position 731.5 km (see Fig. 1) and the three zones of classification of
the river bed. After Schubert (2002).
good quality that permitted drinking water production without fur- down-river of the source. There is one horizontal collector well at
ther treatment, other than disinfection. After 1950, the quality of 730.7 km situated approximately 80 m from the waterline (at mean
the river water began to deteriorate gradually as the impacts of discharge) and 70 vertical filter wells connected by siphon pipes
increasing quantities and insufficient treatment of industrial and that form a well gallery parallel to the riverbank at about 50 m from
municipal effluents became apparent. The consequences of these the waterline. The total length of the well gallery is 1400 m with the
discharges were a noticeable drop in the oxygen concentration, an pumping rate during the field studies roughly constant between 3.0
−1
3
4
increase in the load of organic pollutants and the development of and 3.4 × 10 m day . The aquifer consists of Pleistocene sandy
anoxic conditions in the adjacent aquifer. Moreover, clogging of the gravel sediments with a hydraulic conductivity of between 4 × 10 −3
−2
river bed with particulate organic matter threatened the well yield and 2 × 10 ms −1 and a thickness of approximately 20 m. The
of the riverbank filtration scheme. At this time, the pumped well aquifer is overlain by a 0.5–2 m thick meadow loam and is under-
water had to be treated to remove iron, manganese and ammonium lain by nearly impermeable Tertiary fine sands. The riverbank slope
and, furthermore, micropollutants. These changes prompted field is coated by a 0.5 m thick clay layer above the mean water level of
studies to understand the riverbank filtration process and to better the river and is protected by basalt blocks below the mean water
manage the water supply through the development of calibrated level.
numerical models for the simulation of flow and transport. With the aid of a diving cabin, the 1987 field study identified
An investigation of the river bed conditions and flow and trans- three different zones on the river bed (Fig. 2). Zone 1 nearest the
port processes was carried out in 1987 at the Flehe waterworks, production wells is 80 m wide and is composed of fixed ground that
Düsseldorf. As shown in Fig. 1, the production wells are situated on is fully clogged by suspended solids that form a silt layer. This silt
an outer bend of the River Rhine between 730.7 and 732.1 km layer is formed by mechanical clogging and is almost impermeable