Page 309 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 309
HYDC08 12/5/05 5:31 PM Page 292
292 Chapter Eight
20 hours to 3 months at the site of a riverbank filtra-
tion scheme in south-west Ohio (Sheets et al. 2002),
with shorter and more consistent travel times ob-
tained under conditions of continuous pumping.
Diffuse sources of contamination in catchment
runoff, especially from agricultural activities, can
adversely affect river water quality and therefore
bank filtrate. The study by Grischek et al. (1998)
demonstrated the potential for denitrification at a
sand and gravel aquifer site on the River Elbe in east-
ern Germany where both dissolved and solid organic
carbon within the aquifer act as electron donors.
Verstraeten et al. (2002) reported changes in con-
centrations of triazine and acetamide herbicides at a
well-field on the River Platte in Nebraska and showed
that parent compounds were reduced by 76% of the
river water value (with a third of this due to riverbank
filtration) but that increases in concentrations of
specific metabolite compounds were identified after
riverbank filtration and ozonation treatment.
Polar organic molecules are an increasingly prob-
lematic class of contaminants for riverbank filtration
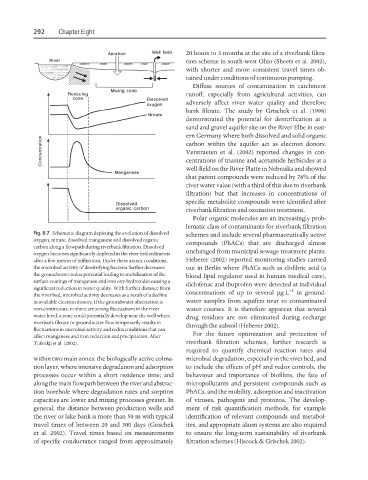
Fig. 8.7 Schematic diagram depicting the evolution of dissolved schemes and include several pharmaceutically active
oxygen, nitrate, dissolved manganese and dissolved organic
compounds (PhACs) that are discharged almost
carbon along a flowpath during riverbank filtration. Dissolved
unchanged from municipal sewage treatment plants.
oxygen becomes significantly depleted in the river bed sediments
after a few metres of infiltration. Under these anoxic conditions, Heberer (2002) reported monitoring studies carried
the microbial activity of denitrifying bacteria further decreases out in Berlin where PhACs such as clofibric acid (a
the groundwater redox potential leading to mobilization of the blood lipid regulator used in human medical care),
surface coatings of manganese and iron oxy-hydroxides causing a
diclofenac and ibuprofen were detected at individual
significant reduction in water quality. With further distance from
concentrations of up to several µgL −1 in ground-
the river bed, microbial activity decreases as a result of a decline
in available electron donors. If the groundwater abstraction is water samples from aquifers near to contaminated
non-continuous, or there are strong fluctuations in the river water courses. It is therefore apparent that several
water level, a zone could potentially develop near the well where drug residues are not eliminated during recharge
riverbank filtrate or groundwater flow temporarily results in
through the subsoil (Heberer 2002).
fluctuations in microbial activity and redox conditions that can
For the future optimization and protection of
affect manganese and iron reduction and precipitation. After
Tufenkji et al. (2002). riverbank filtration schemes, further research is
required to quantify chemical reaction rates and
within two main zones: the biologically active colma- microbial degradation, especially in the river bed, and
tion layer, where intensive degradation and adsorption to include the effects of pH and redox controls, the
processes occur within a short residence time; and behaviour and importance of biofilms, the fate of
along the main flowpath between the river and abstrac- micropollutants and persistent compounds such as
tion borehole where degradation rates and sorption PhACs, and the mobility, adsorption and inactivation
capacities are lower and mixing processes greater. In of viruses, pathogens and protozoa. The develop-
general, the distance between production wells and ment of risk quantification methods, for example
the river or lake bank is more than 50 m with typical identification of relevant compounds and metabol-
travel times of between 20 and 300 days (Grischek ites, and appropriate alarm systems are also required
et al. 2002). Travel times based on measurements to ensure the long-term sustainability of riverbank
of specific conductance ranged from approximately filtration schemes (Hiscock & Grischek 2002).