Page 312 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 312
HYDC08 12/5/05 5:31 PM Page 295
Groundwater resources and environmental management 295
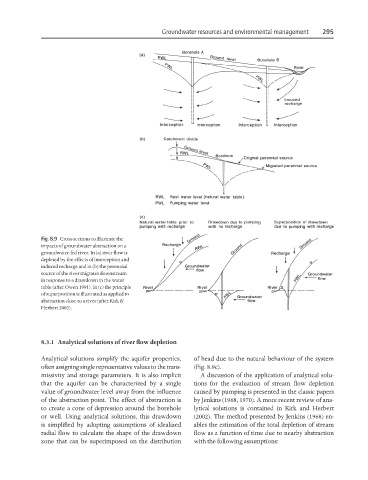
Fig. 8.9 Cross-sections to illustrate the
impacts of groundwater abstraction on a
groundwater-fed river. In (a) river flow is
depleted by the effects of interception and
induced recharge and in (b) the perennial
source of the river migrates downstream
in response to a drawdown in the water
table (after Owen 1991). In (c) the principle
of superposition is illustrated as applied to
abstraction close to a river (after Kirk &
Herbert 2002).
8.3.1 Analytical solutions of river flow depletion
Analytical solutions simplify the aquifer properties, of head due to the natural behaviour of the system
often assigning single representative values to the trans- (Fig. 8.9c).
missivity and storage parameters. It is also implicit A discussion of the application of analytical solu-
that the aquifer can be characterized by a single tions for the evaluation of stream flow depletion
value of groundwater level away from the influence caused by pumping is presented in the classic papers
of the abstraction point. The effect of abstraction is by Jenkins (1968, 1970). A more recent review of ana-
to create a cone of depression around the borehole lytical solutions is contained in Kirk and Herbert
or well. Using analytical solutions, this drawdown (2002). The method presented by Jenkins (1968) en-
is simplified by adopting assumptions of idealized ables the estimation of the total depletion of stream
radial flow to calculate the shape of the drawdown flow as a function of time due to nearby abstraction
zone that can be superimposed on the distribution with the following assumptions: