Page 104 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 104
m
- -
In
- Starting and control of slip-ring induction motors 5/85
I I I 1
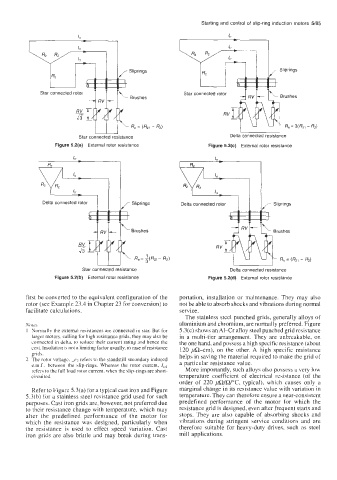
Star connected rotor 1 Star connected rotor J
' Brushes
Star connected resistance
Figure 5.2(a) External rotor resistance
-
17, -
-
-
I,, -
& ( I /-
Delta connected rotor Delta connected rotor
I
Sliprings
Star connected resistance Delta connected resistance
Figure 5.2(b) External rotor resistance Figure 5.2(d) External rotor resistance
first be converted to the equivalent configuration of the portation, installation or maintenance. They may also
rotor (see Example 23.4 in Chapter 23 for conversion) to not be able to absorb shocks and vibrations during normal
facilitate calculations. service.
The stainless steel punched grids, generally alloys of
Notes aluminium and chromium, are normally preferred. Figure
I Normally the external resistances are connected in star. But for 5.3(c) shows an A1-Cr alloy steel punched grid resistance
larger motors, calling for high resistance grids, they may also be in a multi-tier arrangement. They are unbreakable, on
connected in delta, to reduce their current rating and hence the the one hand, and possess a high specific resistance (about
cost. Insulation is not a limiting factor usually, in case of resistance 120 $2-cm), on the other. A high specific resistance
grids. helps in saving the material required to make the grid of
Z The rotor voltage, \,e2 refers to the standstill secondary induced a particular resistance value.
e.m.f.. between the slip-rings. Whereas the rotor current, I,,
refers to the full load rotor current, when the slip-rings are short- More importantly, such alloys also possess a very low
circuited. temperature coefficient of electrical resistance (of the
order of 220 pQIQ/"C, typical), which causes only a
Refer to Figure 5.3(a) for a typical cast iron and Figure marginal change in its resistance value with variation in
5.3(b) for a stainless steel resistance grid used for such temperature. They can therefore ensure a near-consistent
purposes. Cast iron grids are, however, not preferred due predefined performance of the motor for which the
to their resistance change with temperature, which may resistance grid is designed, even after frequent starts and
alter the predefined performance of the motor for stops. They are also capable of absorbing shocks and
which the resistance was designed, particularly when vibrations during stringent service conditions and are
the resistance is used to effect speed variation. Cast therefore suitable for heavy-duty drives, such as steel
iron grids are also brittle and may break during trans- mill applications.