Page 361 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 361
13/336 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
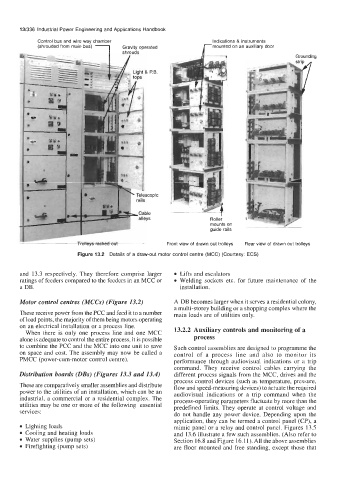
Control bus and wire way chamber Indications & instruments
(shrouded from main bus) 1 rmounted on an auxiliary door
Gravity operated
Grounding
f
j_-
Roller
mounts on /+
guide rails
Trolleys racked out Front view of drawn out trolleys Rear view of drawn out trolleys
Figure 13.2 Details of a draw-out motor control centre (MCC) (Courtesy: ECS)
and 13.3 respectively. They therefore comprise larger Lifts and escalators
ratings of feeders compared to the feeders in an MCC or Welding sockets etc. for future maintenance of the
a DB. installation.
Motor control centres (MCCs) (Figure 13.2) A DB becomes larger when it serves a residential colony,
a multi-storey building or a shopping complex where the
These receive power from the PCC and feed it to a number main loads are of utilities only.
of load points, the majority of them being motors operating
on an electrical installation or a process line. 13.2.2 Auxiliary controls and monitoring of a
When there is only one process line and one MCC
alone is adequate to control the entire process, it is possible process
to combine the PCC and the MCC into one unit to save Such control assemblies are designed to programme the
on space and cost. The assembly may now be called a control of a process line and also to monitor its
PMCC (power-cum-motor control centre). performance through audiovisual indications or a trip
command. They receive control cables carrying the
Distribution boards (DBs) (Figures 13.3 and 13.4) different process signals from the MCC, drives and the
process control devices (such as temperature, pressure,
These are comparatively smaller assemblies and distribute flow and speed-measuring devices) to actuate the required
power to the utilities of an installation, which can be an audiovisual indications or a trip command when the
industrial, a commercial or a residential complex. The process-operating parameters fluctuate by more than the
utilities may be one or more of the following essential predefined limits. They operate at control voltage and
services:
do not handle any power device. Depending upon the
application, they can be termed a control panel (CP), a
Lighting loads mimic panel or a relay and control panel. Figures 13.5
Cooling and heating loads and 13.6 illustrate a few such assemblies. (Also refer to
Water supplies (pump sets) Section 16.8 and Figure 16.11). All the above assemblies
Firefighting (pump sets) are floor mounted and free standing, except those that