Page 366 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 366
Switchgear and controlgear assemblies 13/341
Bushbar will be contained and localized only to the faulty feeder,
chamber Cable box without spreading to the nearby feeders.
13.3.2 Draw-out construction
In this construction each feeder is mounted on a separate
withdrawable chassis as shown in Figures 13.2 and 13.12.
In the event of regular maintenance or repairs, they can
be swiftly racked-out or racked-in to their modules without
disconnecting the incoming or outgoing power connections
or the control terminals*. The modules of identical types
can also be easily interchanged and defective modules
replaced by spare modules in the event of a fault.
Downtime is now low. This arrangement is therefore
recommended for all critical installations that require an
unintermpted power supply and cannot downtime during
operation. It is most suited for installations such as power
stations, refineries, petrochemical plants, fertilizers, and
similar process plants. Similarly, hospitals, airports,
railways, etc. are also such critical areas that may
experience chaos due to a disruption of utilities unless
the normal supply is restored swiftly. In such places this
Cable box type of construction is more appropriate. A draw-out
assembly can be designed only in a cubicle construction
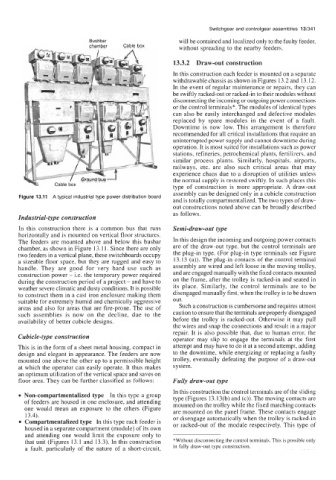
Figure 13.11 A typical industrial type power distribution board
and is totally compartmentalized. The two types of draw-
out constructions noted above can be broadly described
as follows.
Industrial-type construction
In this construction there is a common bus that runs Semi-draw-out type
horizontally and is mounted on vertical floor structures.
The feeders are mounted above and below this busbar In this design the incoming and outgoing power contacts
chamber, as shown in Figure 13.11. Since there are only are of the draw-out type, but the control terminals are
two feeders in a vertical plane, these switchboards occupy the plug-in type. (For plug-in type terminals see Figure
a sizeable floor space, but they are rugged and easy to 13.13 (a)). The plug-in contacts of the control terminal
handle. They are good for very hard use such as assembly are wired and left loose in the moving trolley,
construction power - i.e. the temporary power required and are engaged manually with the fixed contacts mounted
during the construction period of a project - and have to on the frame, after the trolley is racked-in and seated in
weather severe climatic and dusty conditions. It is possible its place. Similarly, the control terminals are to be
to construct them in a cast iron enclosure making them disengaged manually first, when the trolley is to be drawn
suitable for extremely humid and chemically aggressive out.
areas and also for areas that are fire-prone. The use of Such a construction is cumbersome and requires utmost
such assemblies is now on the decline, due to the caution to ensure that the terminals are properly disengaged
availability of better cubicle designs. before the trolley is racked-out. Otherwise it may pull
the wires and snap the connections and result in a major
repair. It is also possible that, due to human error, the
Cubicle-type construction operator may slip to engage the terminals at the first
This is in the form of a sheet metal housing, compact in attempt and may have to do it at a second attempt, adding
design and elegant in appearance. The feeders are now to the downtime, while energizing or replacing a faulty
mounted one above the other up to a permissible height trolley, eventually defeating the purpose of a draw-out
at which the operator can easily operate. It thus makes system.
an optimum utilization of the vertical space and saves on
floor area. They can be further classified as follows: Fully draw-out type
In this construction the control terminals are of the sliding
Non-compartmentalized type In this type a group type (Figures 13.13(b) and (c)). The moving contacts are
of feeders are housed in one enclosure, and attending mounted on the trolley while the fixed matching contacts
one would mean an exposure to the others (Figure are mounted on the panel frame. These contacts engage
13.4). or disengage automatically when the trolley is racked-in
Compartmentalized type In this type each feeder is or racked-out of the module respectively. This type of
housed in a separate compartment (module) of its own
and attending one would limit the exposure only to
that unit (Figures 13.1 and 13.3). In this construction *Without disconnecting the control terminals. This is possible only
a fault, particularly of the nature of a short-circuit, in fully draw-out type construction.