Page 583 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 583
16/548 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
x =0.076 for PVC cables*
A Cable to be
= 0.078 for paper insulated cables,* and suitable for system
= 0.094 for XLPE cables etc*.
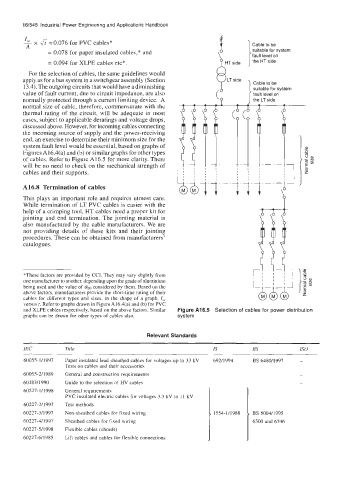
For the selection of cables, the same guidelines would
apply as for a bus system in a switchgear assembly (Section Cable to be
13.4). The outgoing circuits that would have a diminishing suitable for system
value of fault current, due to circuit impedance, are also fault level on
normally protected through a current limiting device. A the LT side
normal size of cable, therefore, commensurate with the I
thermal rating of the circuit, will be adequate in most
cases, subject to applicable deratings and voltage drops,
discussed above. However, for incoming cables connecting
the incoming source of supply and the power-receiving
end, an exercise to determine their minimum size for the
system fault level would be essential, based on graphs of
FiguresA16.4(a) and (b) or similar graphs for other types
of cables. Refer to Figure A16.5 for more clarity. There
will be no need to check on the mechanical strength of e-/n .~
cables and their supports.
A16.8 Termination of cables
This plays an important role and requires utmost care.
While termination of LT PVC cables is easier with the
help of a crimping tool, HT cables need a proper kit for
jointing and end termination. The jointing material is
also manufactured by the cable manufacturers. We are
not providing details of these kits and their jointing
procedures. These can be obtained from manufacturers'
catalogues.
*These factors are provided by CCI. They may vary slightly from
one manufacturer to another, depending upon the grade of aluminium
being used and the value of q, considered by them. Based on the
above tactors, manufacturers provide the short-time rating of their
cables for different types and sizes, in the shape of a graph, I,,
versus t. Refer to graphs drawn in FigureA16.4(a) and (b) for PVC
and XLPE cables respectively, based on the above factors. Similar Figure A16.5 Selection of
graphs can be drawn for other types of cables also. system
Relevant Standards
~
IEC Title IS BS IS0
60055-l/1997 Paper insulated lead sheathed cables for voltages up to 33 kV 692/1994 BS 6480/1997 -
Tests on cables and their accessories
6005 5 -2/ 1 9 89 General and construction requirements
60 183/1990 Guide to the selection of HV cables
60227- 1/1998 General requirements
PVC insulated electric cables for voltages 3.3 kV to 11 kV
60227-2/1997 Test methods
60227-3/1997 Non-sheathed cables for fixed wiring s 1554-1/1988 . BS 6004/1995
60227-4/1997 Sheathed cables for fixed wiring 6500 and 6746
60227-5/1998 Flexible cables (chords)
60227-6/1985 Lift cables and cables for flexible connections