Page 773 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 773
23/730 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
II I
Voltaoe wave ’P‘
Switch recovery
3rd interruption
i
c“
I cycle I cycle
(90” leading)
\ I I
2nd current 3rd current
zero zero zero
1st 1 st 2nd
interruption restrike restrike
Time --m
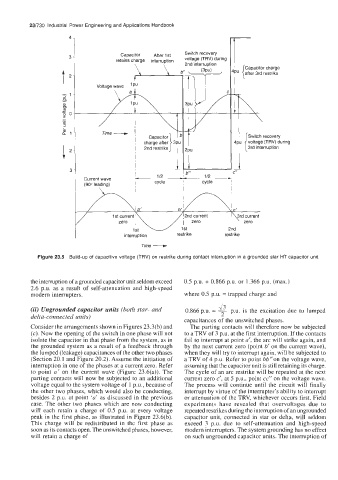
Figure 23.5 Build-up of capacitive voltage (TRV) on restrike during contact interruption in a grounded star HT capacitor unit
the interruption of a grounded capacitor unit seldom exceed 0.5 p.u. + 0.866 p.u. or 1.366 p.u. (max.)
2.6 p.u. as a result of self-attenuation and high-speed
modern interrupters. where 0.5 p.u. = trapped charge and
217
(ii) Ungrounded capacitor units (both star- and 0.866 p.u. = 7 p.u. is the excitation due to lumped
delta-connected units) I
capacitances of the unswitched phases.
Consider the arrangements shown in Figures 23.3(b) and The parting contacts will therefore now be subjected
(c). Now the opening of the switch in one phase will not to a TRV of 3 p.u. at the first interruption. If the contacts
isolate the capacitor in that phase from the system, as in fail to interrupt at point a’, the arc will strike again, and
the grounded system as a result of a feedback through by the next current zero (point b’ on the current wave),
the lumped (leakage) capacitances of the other two phases when they will try to interrupt again, will be subjected to
(Section 20.1 and Figure 20.2). Assume the initiation of a TRV of 4 p.u. Refer to point bb”on the voltage wave,
interruption in one of the phases at a current zero. Refer assuming that the capacitor unit is still retaining its charge.
to point a’ on the current wave (Figure 23.6(a)). The The cycle of an arc restrike will be repeated at the next
parting contacts will now be subjected to an additional current zero c’, at 5 P.u., point cc” on the voltage wave.
voltage equal to the system voltage of 1 P.u., because of The process will continue until the circuit will finally
the other two phases, which would also be conducting, interrupt by virtue of the interrupter’s ability to interrupt
besides 2 p.u. at point ‘a’ as discussed in the previous or attenuation of the TRV, whichever occurs first. Field
case. The other two phases which are now conducting experiments have revealed that overvoltages due to
will each retain a charge of 0.5 p.u. at every voltage repeated restrikes during the interruption of an ungrounded
peak in the first phase, as illustrated in Figure 23.6(b). capacitor unit, connected in star or delta, will seldom
This charge will be redistributed in the first phase as exceed 3 p.u. due to self-attenuation and high-speed
soon as its contacts open. The unswitched phases, however, modern interrupters. The system grounding has no effect
will retain a charge of on such ungrounded capacitor units. The interruption of