Page 223 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 223
Advanced Treatment Technology and Strategy 197
Oxidant Catalyst
Treated water
Oxidation
Wastewater storage reactor
tank
Exhausted catalyst
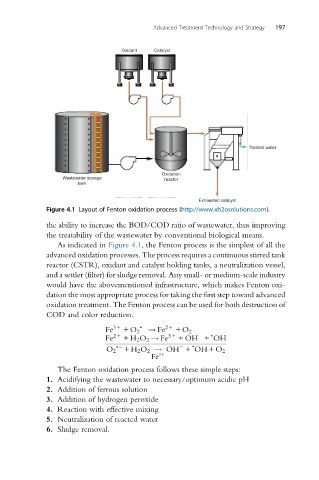
Figure 4.1 Layout of Fenton oxidation process (http://www.xh2osolutions.com).
the ability to increase the BOD/COD ratio of wastewater, thus improving
the treatability of the wastewater by conventional biological means.
As indicated in Figure 4.1, the Fenton process is the simplest of all the
advanced oxidation processes. The process requires a continuous stirred tank
reactor (CSTR), oxidant and catalyst holding tanks, a neutralization vessel,
and a settler (filter) for sludge removal. Any small- or medium-scale industry
would have the abovementioned infrastructure, which makes Fenton oxi-
dation the most appropriate process for taking the first step toward advanced
oxidation treatment. The Fenton process can be used for both destruction of
COD and color reduction.
Fe 3+ +O 2 • ! Fe 2+ +O 2
•
Fe 2+ +H 2 O 2 ! Fe 3+ +OH + OH
• •
O 2 +H 2 O 2 ! OH + OH + O 2
Fe 3+
The Fenton oxidation process follows these simple steps:
1. Acidifying the wastewater to necessary/optimum acidic pH
2. Addition of ferrous solution
3. Addition of hydrogen peroxide
4. Reaction with effective mixing
5. Neutralization of reacted water
6. Sludge removal.