Page 224 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 224
198 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
Principal advantages of Fenton oxidation are the following:
1. Simple process, can be conducted in either batch or continuous mode
2. Readily available chemicals for treatment
3. Completely green, environmentally friendly process
4. Destroys a very broad range of organic compounds
5. Can be a pre- or posttreatment step for a biological process
6. Sludge generated is completely nonhazardous and can be safely
disposed of.
The disadvantages of the Fenton process are the following:
1. Large quantity of sludge generated
2. Difficulty of hydrogen peroxide management
3. The problem of identifying optimum dosages for cost-effective
treatment.
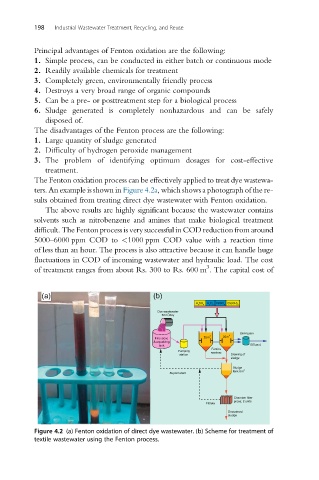
The Fenton oxidation process can be effectively applied to treat dye wastewa-
ters. An example is shown in Figure 4.2a, which shows a photograph of the re-
sults obtained from treating direct dye wastewater with Fenton oxidation.
The above results are highly significant because the wastewater contains
solvents such as nitrobenzene and amines that make biological treatment
difficult. The Fenton process is very successful in COD reduction from around
5000–6000 ppm COD to <1000 ppm COD value with a reaction time
of less than an hour. The process is also attractive because it can handle huge
fluctuations in COD of incoming wastewater and hydraulic load. The cost
3
of treatment ranges from about Rs. 300 to Rs. 600 m . The capital cost of
(a) (b)
H 2 SO 4 H 2 O 2 FeSO 4 Ca(OH) 2
Dye wastewater
3
50m /day
Sink basin
3 3
Fine sieve 25m 25m
& equalizing
tank Effluent
Fenton
Pumping reactors
station Draining of
sludge
Sludge 3
tank 6m
Supernatant
Chamber filter
press; 2 units
Filtrate
Dewatered
sludge
Figure 4.2 (a) Fenton oxidation of direct dye wastewater. (b) Scheme for treatment of
textile wastewater using the Fenton process.