Page 229 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 229
Advanced Treatment Technology and Strategy 203
the oxidation process, without getting converted into sludge. The principal
advantages of the Fenton catalytic reactor process are less sludge formation,
suitability for treatment of high volumes of wastewater, nonselective oxida-
tion of organics, and its ability to be an effective polishing step for CETPs,
municipal sewage treatment, and other uses.
Almost all the efforts in developing the Fenton process have aimed at the
reduction of sludge formation during the course of the reaction. The Fenton
catalytic reaction process, also known as the fluidized-bed Fenton process, was
developed by ITRI (Haung etal.,2000;Yao-Hui etal.,2000). Although the
Fenton process has been successful in the degradation of organic contaminants
present in wastewater, the production of ferric hydroxide sludge in the form
of Fe(OH) 3 is considered to be a disadvantage of this process, requires further
separation and disposal. One of the alternatives for dealing with this problem is
the use of the fluidized-bed Fenton reactor. The carriers in the fluidized-bed
Fenton reactor can initiate the iron precipitation and/or crystallization pro-
cess; therefore, the production of sludge can be reduced. Several reactions
occur during the operation of the fluidized-bed Fenton reactor, including
2+
(1) homogeneous chemical oxidation (H 2 O 2 /Fe ), (2) heterogeneous
chemical oxidation (H 2 O 2 /iron oxide), (3) fluidized-bed crystallization,
and (4) reductive dissolution of iron oxides (Muangthai et al., 2010).
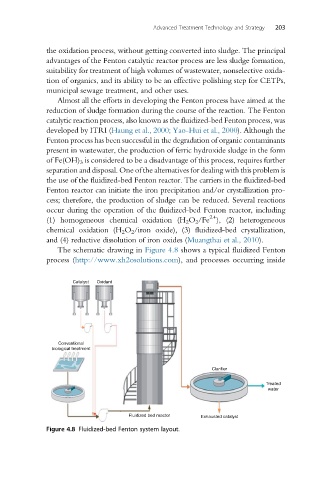
The schematic drawing in Figure 4.8 shows a typical fluidized Fenton
process (http://www.xh2osolutions.com), and processes occurring inside
Catalyst Oxidant
Conventional
biological treatment
Clarifier
Treated
water
Fluidized bed reactor Exhausted catalyst
Figure 4.8 Fluidized-bed Fenton system layout.