Page 238 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 238
212 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
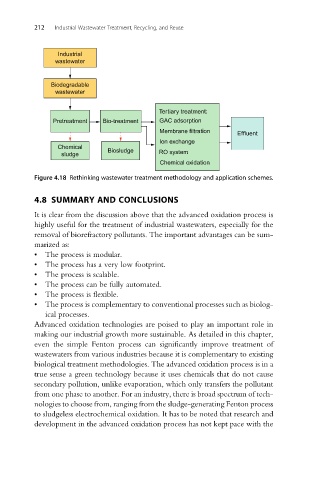
Industrial
wastewater
Biodegradable
wastewater
Tertiary treatment:
Pretreatment Bio-treatment GAC adsorption
Membrane filtration Effluent
Ion exchange
Chemical Biosludge
sludge RO system
Chemical oxidation
Figure 4.18 Rethinking wastewater treatment methodology and application schemes.
4.8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
It is clear from the discussion above that the advanced oxidation process is
highly useful for the treatment of industrial wastewaters, especially for the
removal of biorefractory pollutants. The important advantages can be sum-
marized as:
• The process is modular.
• The process has a very low footprint.
• The process is scalable.
• The process can be fully automated.
• The process is flexible.
• The process is complementary to conventional processes such as biolog-
ical processes.
Advanced oxidation technologies are poised to play an important role in
making our industrial growth more sustainable. As detailed in this chapter,
even the simple Fenton process can significantly improve treatment of
wastewaters from various industries because it is complementary to existing
biological treatment methodologies. The advanced oxidation process is in a
true sense a green technology because it uses chemicals that do not cause
secondary pollution, unlike evaporation, which only transfers the pollutant
from one phase to another. For an industry, there is broad spectrum of tech-
nologies to choose from, ranging from the sludge-generating Fenton process
to sludgeless electrochemical oxidation. It has to be noted that research and
development in the advanced oxidation process has not kept pace with the