Page 242 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 242
216 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
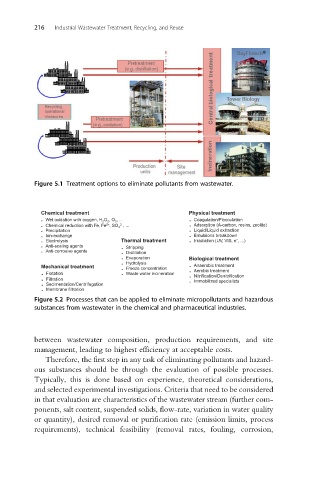
Figure 5.1 Treatment options to eliminate pollutants from wastewater.
Chemical treatment Physical treatment
. Wet oxidation with oxygen, H 2 O 2 , O 3 , ... . Coagulation/Flocculation
2+
2−
. Chemical reduction with Fe, Fe , SO 3 , ... . Adsorption (A-carbon, resins, zeolite)
. Precipitation . Liquid/Liquid extraction
. Ion-exchange . Emulsions breakdown
−
. Electrolysis Thermal treatment . Irradiation (UV, VIS, e , ...)
. Anti-scaling agents . Stripping
. Anti-corrosive agents . Distillation
. Evaporation Biological treatment
. Hydrolysis
Mechanical treatment . Freeze concentration . Anaerobic treatment
. Flotation . Waste water incineration . Aerobic treatment
. Nitrification/Denitrification
. Filtration . Immobilized specialists
. Sedimentation/Centrifugation
. Membrane filtration
Figure 5.2 Processes that can be applied to eliminate micropollutants and hazardous
substances from wastewater in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
between wastewater composition, production requirements, and site
management, leading to highest efficiency at acceptable costs.
Therefore, the first step in any task of eliminating pollutants and hazard-
ous substances should be through the evaluation of possible processes.
Typically, this is done based on experience, theoretical considerations,
and selected experimental investigations. Criteria that need to be considered
in that evaluation are characteristics of the wastewater stream (further com-
ponents, salt content, suspended solids, flow-rate, variation in water quality
or quantity), desired removal or purification rate (emission limits, process
requirements), technical feasibility (removal rates, fouling, corrosion,