Page 401 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 401
An Introduction to Biological Treatment and Membrane Filtration 373
Organic contaminants
Methane
Nutrients
Anaerobic
bacteria
Carbon dioxide
New cells
Anaerobic principle
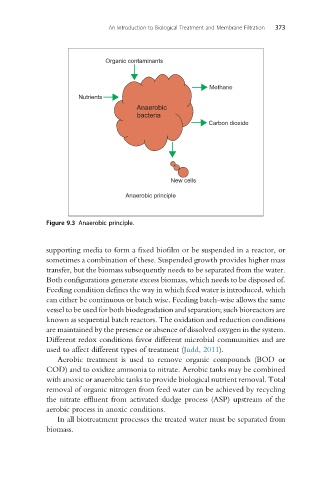
Figure 9.3 Anaerobic principle.
supporting media to form a fixed biofilm or be suspended in a reactor, or
sometimes a combination of these. Suspended growth provides higher mass
transfer, but the biomass subsequently needs to be separated from the water.
Both configurations generate excess biomass, which needs to be disposed of.
Feeding condition defines the way in which feed water is introduced, which
can either be continuous or batch wise. Feeding batch-wise allows the same
vessel to be used for both biodegradation and separation; such bioreactors are
known as sequential batch reactors. The oxidation and reduction conditions
are maintained by the presence or absence of dissolved oxygen in the system.
Different redox conditions favor different microbial communities and are
used to affect different types of treatment (Judd, 2011).
Aerobic treatment is used to remove organic compounds (BOD or
COD) and to oxidize ammonia to nitrate. Aerobic tanks may be combined
with anoxic or anaerobic tanks to provide biological nutrient removal. Total
removal of organic nitrogen from feed water can be achieved by recycling
the nitrate effluent from activated sludge process (ASP) upstream of the
aerobic process in anoxic conditions.
In all biotreatment processes the treated water must be separated from
biomass.