Page 431 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 431
Application of Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor 403
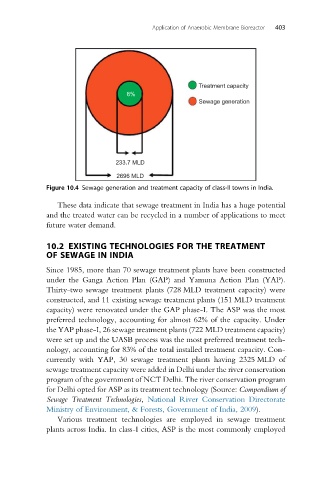
Treatment capacity
8%
Sewage generation
233.7 MLD
2696 MLD
Figure 10.4 Sewage generation and treatment capacity of class-II towns in India.
These data indicate that sewage treatment in India has a huge potential
and the treated water can be recycled in a number of applications to meet
future water demand.
10.2 EXISTING TECHNOLOGIES FOR THE TREATMENT
OF SEWAGE IN INDIA
Since 1985, more than 70 sewage treatment plants have been constructed
under the Ganga Action Plan (GAP) and Yamuna Action Plan (YAP).
Thirty-two sewage treatment plants (728 MLD treatment capacity) were
constructed, and 11 existing sewage treatment plants (151 MLD treatment
capacity) were renovated under the GAP phase-I. The ASP was the most
preferred technology, accounting for almost 62% of the capacity. Under
the YAP phase-I, 26 sewage treatment plants (722 MLD treatment capacity)
were set up and the UASB process was the most preferred treatment tech-
nology, accounting for 83% of the total installed treatment capacity. Con-
currently with YAP, 30 sewage treatment plants having 2325 MLD of
sewage treatment capacity were added in Delhi under the river conservation
program of the government of NCT Delhi. The river conservation program
for Delhi opted for ASP as its treatment technology (Source: Compendium of
Sewage Treatment Technologies, National River Conservation Directorate
Ministry of Environment, & Forests, Government of India, 2009).
Various treatment technologies are employed in sewage treatment
plants across India. In class-I cities, ASP is the most commonly employed