Page 192 - Instant notes
P. 192
Physical chemistry 178
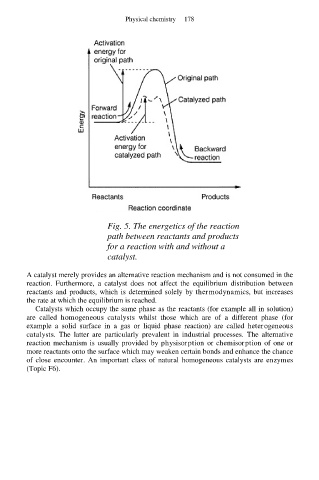
Fig. 5. The energetics of the reaction
path between reactants and products
for a reaction with and without a
catalyst.
A catalyst merely provides an alternative reaction mechanism and is not consumed in the
reaction. Furthermore, a catalyst does not affect the equilibrium distribution between
reactants and products, which is determined solely by thermodynamics, but increases
the rate at which the equilibrium is reached.
Catalysts which occupy the same phase as the reactants (for example all in solution)
are called homogeneous catalysts whilst those which are of a different phase (for
example a solid surface in a gas or liquid phase reaction) are called heterogeneous
catalysts. The latter are particularly prevalent in industrial processes. The alternative
reaction mechanism is usually provided by physisorption or chemisorption of one or
more reactants onto the surface which may weaken certain bonds and enhance the chance
of close encounter. An important class of natural homogeneous catalysts are enzymes
(Topic F6).