Page 188 - Instant notes
P. 188
Physical chemistry 174
which is exactly the form of the Arrhenius equation with the constant of proportionality
identifiable as the pre-exponential Arrhenius factor A.
The value of A can be calculated using the kinetic theory of gases by assuming that
two hard spheres collide when the distance between them is less than the sum of their
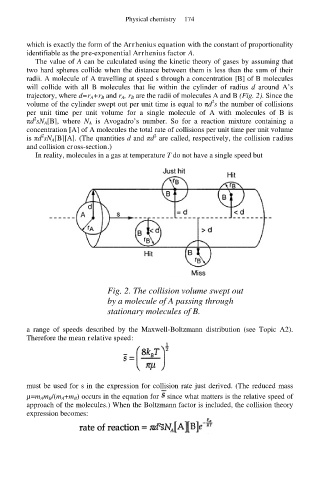
radii. A molecule of A travelling at speed s through a concentration [B] of B molecules
will collide with all B molecules that lie within the cylinder of radius d around A’s
trajectory, where d=r A+r B and r A, r B are the radii of molecules A and B (Fig. 2). Since the
2
volume of the cylinder swept out per unit time is equal to πd s the number of collisions
per unit time per unit volume for a single molecule of A with molecules of B is
2
πd sN A[B], where N A is Avogadro’s number. So for a reaction mixture containing a
concentration [A] of A molecules the total rate of collisions per unit time per unit volume
2
2
is πd sN A[B][A]. (The quantities d and πd are called, respectively, the collision radius
and collision cross-section.)
In reality, molecules in a gas at temperature T do not have a single speed but
Fig. 2. The collision volume swept out
by a molecule of A passing through
stationary molecules of B.
a range of speeds described by the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution (see Topic A2).
Therefore the mean relative speed:
must be used for s in the expression for collision rate just derived. (The reduced mass
µ=m Am B/(m A+m B) occurs in the equation for since what matters is the relative speed of
approach of the molecules.) When the Boltzmann factor is included, the collision theory
expression becomes: