Page 183 - Instant notes
P. 183
Rate law determination 169
For reactions of this type a straight line is obtained from a plot of ln([B]/[A]) against t
(Table 1) and the gradient of the line corresponds to k([B] 0−[A] 0). However, to undertake
such an analysis requires measurement of the absolute concentrations of both A and B
simultaneously so, where possible, experimental conditions are arranged such that either
[A] 0=[B] 0, in which case the mathematics of the kinetics is the same as the second order
integration in A given above, or that (or υice υersa), in which case the
reaction reduces to pseudo-first order kinetics. The second approach yields the pseudo-
first order rate constant, k′=k[B] 0, without needing to know absolute concentrations (from
the plot of the natural logarithm of relative concentration of A with time) but the true
second order rate constant is only obtained by repeating measurements
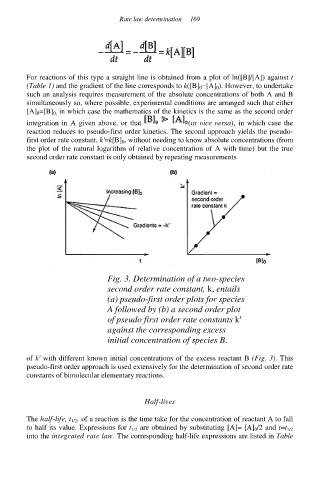
Fig. 3. Determination of a two-species
second order rate constant, k, entails
(a) pseudo-first order plots for species
A followed by (b) a second order plot
of pseudo first order rate constants k′
against the corresponding excess
initial concentration of species B.
of k′ with different known initial concentrations of the excess reactant B (Fig. 3). This
pseudo-first order approach is used extensively for the determination of second order rate
constants of bimolecular elementary reactions.
Half-lives
The half-life, t 1/2, of a reaction is the time take for the concentration of reactant A to fall
to half its value. Expressions for t 1/2 are obtained by substituting [A]= [A] 0/2 and t=t 1/2
into the integrated rate law. The corresponding half-life expressions are listed in Table