Page 357 - Instant notes
P. 357
Photochemistry in the real world 343
molecules and ions in electronically excited states which emit visible fluorescence as they
return to the ground state.
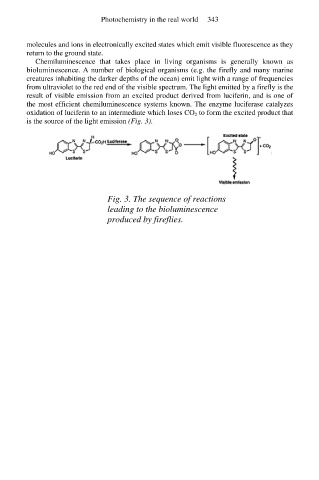
Chemiluminescence that takes place in living organisms is generally known as
bioluminescence. A number of biological organisms (e.g. the firefly and many marine
creatures inhabiting the darker depths of the ocean) emit light with a range of frequencies
from ultraviolet to the red end of the visible spectrum. The light emitted by a firefly is the
result of visible emission from an excited product derived from luciferin, and is one of
the most efficient chemiluminescence systems known. The enzyme luciferase catalyzes
oxidation of luciferin to an intermediate which loses CO 2 to form the excited product that
is the source of the light emission (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3. The sequence of reactions
leading to the bioluminescence
produced by fireflies.