Page 314 - Solutions Manual to accompany Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 314
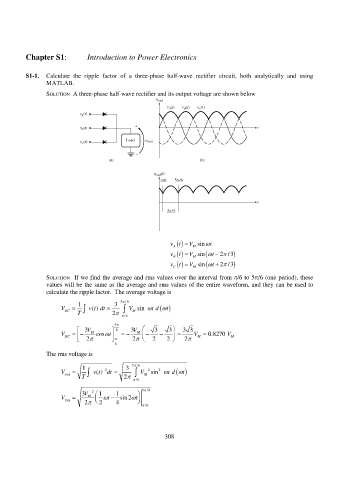
Chapter S1: Introduction to Power Electronics
S1-1. Calculate the ripple factor of a three-phase half-wave rectifier circuit, both analytically and using
MATLAB.
SOLUTION A three-phase half-wave rectifier and its output voltage are shown below
/6 5/6
2/3
V
vt M sin t
A
V
vt M sin t 2 / 3
B
V
vt M sin t 2 / 3
C
SOLUTION If we find the average and rms values over the interval from /6 to 5/6 (one period), these
values will be the same as the average and rms values of the entire waveform, and they can be used to
calculate the ripple factor. The average voltage is
1 3 5/ 6
V DC v () t dt V M sin t d t
2
T
/6
5
3V 6 3V 3 3 3 3
V DC 2 M cos t 2 M 2 2 2 V 0.8270 V
M
M
6
The rms voltage is
1 3 5/ 6
2
V v () t 2 dt V 2 sin t d t
rms M
T 2 /6
3V M 2 1 1 5/ 6
V t sin2 t
rms 2 2 4 /6
308