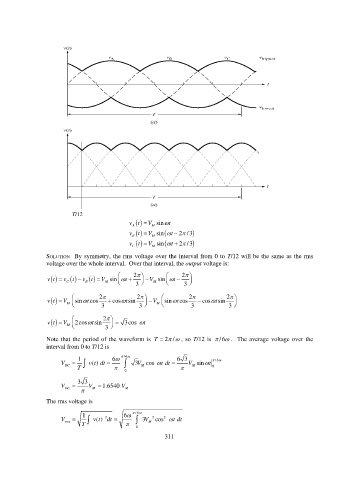
Page 317 - Solutions Manual to accompany Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 317
T/12
V
vt M sin t
A
V
vt M sin t 2 / 3
B
V
vt M sin t 2 / 3
C
SOLUTION By symmetry, the rms voltage over the interval from 0 to T/12 will be the same as the rms
voltage over the whole interval. Over that interval, the output voltage is:
2 2
v t v C t v B t V M sin t 3 V M sin t 3
2 2 2 2
vt V M sin t cos 3 cos t sin 3 V M sin t cos 3 cos t sin 3
2
vt V M 2cos t sin 3 3cos t
Note that the period of the waveform is T 2/ , so T/12 is /6 . The average voltage over the
interval from 0 to T/12 is
1 6 /6 6 3 /6
V DC v () t dt 3V M cos t dt V M sin t
T 0
0
33
V DC V M 1.6540 V
M
The rms voltage is
1 6 /6
2
t
V v () t 2 dt 3V 2 cos dt
rms M
T
0
311