Page 325 - Solutions Manual to accompany Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 325
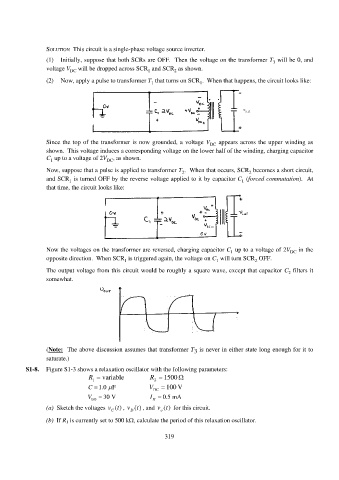
SOLUTION This circuit is a single-phase voltage source inverter.
(1) Initially, suppose that both SCRs are OFF. Then the voltage on the transformer T will be 0, and
3
voltage V DC will be dropped across SCR and SCR as shown.
1
2
(2) Now, apply a pulse to transformer T that turns on SCR . When that happens, the circuit looks like:
1
1
Since the top of the transformer is now grounded, a voltage V DC appears across the upper winding as
shown. This voltage induces a corresponding voltage on the lower half of the winding, charging capacitor
C up to a voltage of 2V DC , as shown.
1
Now, suppose that a pulse is applied to transformer T . When that occurs, SCR becomes a short circuit,
2
2
and SCR is turned OFF by the reverse voltage applied to it by capacitor C (forced commutation). At
1
1
that time, the circuit looks like:
Now the voltages on the transformer are reversed, charging capacitor C up to a voltage of 2V DC in the
1
opposite direction. When SCR is triggered again, the voltage on C will turn SCR OFF.
1
2
1
The output voltage from this circuit would be roughly a square wave, except that capacitor C filters it
2
somewhat.
(Note: The above discussion assumes that transformer T is never in either state long enough for it to
3
saturate.)
S1-8. Figure S1-3 shows a relaxation oscillator with the following parameters:
R variable R 2 1500
1
C 1.0 F V DC 100 V
V BO 30 V I 0.5 mA
H
(a) Sketch the voltages v t() vt() , and vt() for this circuit.
,
o
D
C
(b) If R 1 is currently set to 500 k, calculate the period of this relaxation oscillator.
319