Page 123 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 123
108 Measurement of force
suitable for both static and dynamic force practice, this method may be used for measuring
measurement. The range of this type of instru- dynamic forces associated with vibrating masses,
ment is from 0.1 N to about 1 kN. It is normally and is discussed further in Chapter 6.
bulky and heavy and tends to be expensive.
7.7 Elastic elements
7.5 Hydraulic pressure
measurement A measuring system basically consists of three
elements; a transducer, a signal conditioner, and
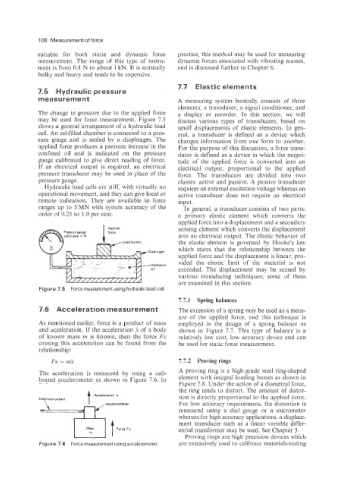
The change in pressure due to the applied force a display or recorder. In this section. we will
may be used for force measurement. Figure 7.5 discuss various types of transducers, based on
shows a general arrangement of a hydraulic load small displacements of elastic elements. In gen-
cell. An oil-filled chamber is connected to a pres- eral, a transducer is defined as a device which
sure gauge and is sealed by a diaphragm. The changes information from one form to another.
applied force produces a pressure increase in the For the purpose of this discussion, a force trans-
confined oil and is indicated on the pressure ducer is defined as a device in which the magni-
gauge calibrated to give direct reading of force. tude of the applied force is converted into an
If an electrical output is required, an electrical electrical output, proportional to the applied
pressure transducer may be used in place of the force. The transducers are divided into two
pressure gauge. classes: active and passive. A passive transducer
Hydraulic load cells are stiff, with virtually no requires an external excitation voltage whereas an
operational movement, and they can give local or active transducer does not require an electrical
remote indication. They are available in force input.
ranges up to 5MN with system accuracy of the In general, a transducer consists of two parts:
order of 0.25 to 1.0 per cent. a primary elastic element which converts the
applied force into a displacement and a secondary
sensing element which converts the displacement
into an electrical output. The elastic behavior of
the elastic element is governed by Hooke's law
which states that the relationship between the
'Diaphragm
applied force and the displacement is linear, pro-
vided the elastic limit of the material is not
-Hydraulic
oil exceeded. The displacement may be sensed by
various transducing techniques; some of them
are examined in this section.
Figure 7.5 Force measurement using hydraulic load cell.
7.7.1 Spring balances
7.6 Acceleration me as u re me n t The extension of a spring may be used as a meas-
ure of the applied force, and this technique is
As mentioned earlier, force is a product of mass employed in the design of a spring balance as
and acceleration If the acceleration x of a body shown in Figure 7.7. This type of balance is a
of known mass in is known, then the force Fx relatively low cost, low accuracy device and can
causing this acceleration can be found from the be used for static force measurement.
relationship:
FX = inx 7.7.2 Proving rings
The acceleration is measured by using a cali- A proving ring is a high-grade steel ring-shaped
brated accelerometer as shown in Figure 7.6. In element with integral loading bosses as shown in
Figure 7.8. Under the action of a diametral force,
t Acceleration x the ring tends to distort. The amount of distor-
tion is directly proportional to the applied force.
Electrical output Accelerometer For low accuracy requirements, the distortion is
I I whereas for high accuracy applications, a displace-
measured using a dial gauge or a micrometer
ment transducer such as a linear variable differ-
My
Force Fx
ential transformer may be used. See Chapter 3.
Proving rings are high precision devices which
Figure 7.6 Force measurement using accelerometer. are extensively used to calibrate materials-testing