Page 444 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 444
Units and standards of electrical measurement 427
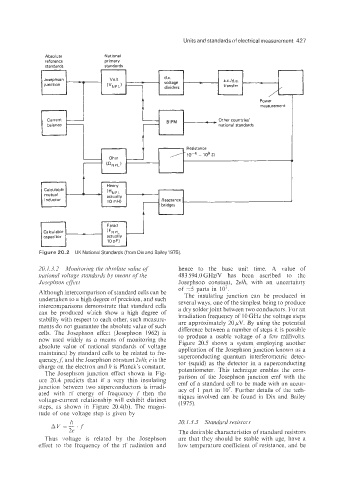
Absolute National
reference primary
standards standards
Power
measurement
Other countries’
national standards
i
Figure 20.2 UK National Standards (from Dixand Bailey1975).
20.1.3.2 ~Wonitoring the absolute value of hence to the base unit time. A value of
izational voltage standards by means of the 483 594.0 GHz/V has been ascribed to the
Joseplzson effect Josephson constant, 2ellz, with an uncertainty
of &5 parts in io7.
Although intercomparison of standard cells can be The insulating junction can be produced in
undertaken to a high degree of precision, and such several ways, one of the simplest being to produce
intercomparisons demonstrate that standard cells a dry solder joint between two conductors. For an
can be produced which show a high degree of irradiation frequency of 10 GHz the voltage steps
stability with respect to each other, such measure- are approximately 20 pV. By using the potential
ments do not guarantee the absolute value of such difference between a number of steps it is possible
cells. The Josephson effect (Josephson 1962) is to produce a usable voltage of a few millivolts.
now used widely as a means of monitoring the Figure 20.5 shows a system employing another
absolute value of national standards of voltage application of the Josephson junction known as a
maintained by standard cells to be related to fre- superconducting quantum interferometric detec-
quency,f, and the Josephson constant 2ellz; e is the tor (squid) as the detector in a superconducting
charge on the electron and h is Planck’s constant. potentiometer. This technique enables the com-
The Josephson junction effect shown in Fig- parison of the Josephson junction emf with the
ure 20.4 predicts that if a very thin insulating emf of a standard cell to be made with an accur-
junction between two superconductors is irradi- acy of 1 part in lo7. Further details of the tech-
ated with rf energy of frequency f then the niques involved can be found in Dix and Bailey
voltage-current relationship will exhibit distinct (1975).
steps, as shown in Figure 20.4(b). The magni-
tude of one voltage step is given by
h 20.1.3.3 Standard resistors
av=- ..f
2e The desirable characteristics of standard resistors
Thus voltage is related by the Josephson are that they should be stable with age. have a
effect to the frequency of the rf radiation and low temperature coefficient of resistance, and be