Page 447 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 447
430 Electrical measurements
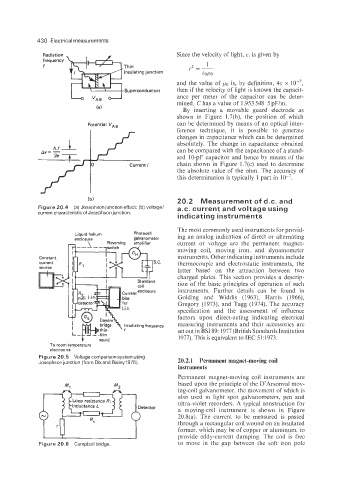
Radiation Since the velocity of light, c, is given by
frequency
f Thin
insulating junction
and the value of PO is, by definition, 47r x lo-',
Superconductors then if the velocity of light is known the capacit-
ance per meter of the capacitor can be deter-
mined. C has a value of 1.953 548 5 pF/m.
By inserting a movable guard electrode as
shown in Figure 1.7(b), the position of which
Potential V,, can be determined by means of an optical inter-
ference technique, it is possible to generate
changes in capacitance which can be determined
absolutely. The change in capacitance obtained
Av= - can be compared with the capacitance of a stand-
h. f
2e 7
ard IO-pF capacitor and hence by means of the
0 Current i chain shown in Figure 1.7(c) used to determine
the absolute value of the ohm. The accuracy of
this determination is typically 1 part in lo-'.
(b) 20.2 Measurement of d.c. and
Figure 20.4 (a) Josephson junction effect; (b) voltage/ a.c. current and voltage using
current characteristic of Josephson junction.
indicating instruments
The most commonly used instruments for provid-
M;;l--r$ys.c,
Photocell
Liquid helium
ing an analog indication of direct or alternating
galvanometer
enclosure
current or voltage are the permanent magnet-
moving coil, moving iron, and dynamometer
Constant instruments. Other indicating instruments include
current thermocouple and electrostatic instruments, the
source
I L latter based on the attraction between two
charged plates. This section provides a descrip-
tion of the basic principles of operation of such
instruments. Further details can be found in
wrrenr
bias Golding and Widdis (1963); Harris (1966),
for Gregory (1 973), and Tagg (1 974). The accuracy
jjs.
specification and the assessment of influence
factors upon direct-acting indicating electrical
,,:;le" \ :radiating frequency measuring instruments and their accessories are
set out in BSI 89: 1977 (British Standards Institution
squid 1977). This is equivalent to IEC 51:1973.
To room-temperature
electronics
Figure 20.5 Voltage comparison system using
Josephson junction (from Dixand Bailey1975). 20.2.1 Permanent magnet-moving coil
instruments
Permanent magnet-moving coil instruments are
based upon the principle of the D'Arsonval mov-
ing-coil galvanometer, the movement of which is
also used in light spot galvanometers, pen and
ultra-violet recorders. A typical construction for
a moving-coil instrument is shown in Figure
20.8(a). The current to be measured is passed
through a rectangular coil wound on an insulated
r
former, which may be of copper or aluminum, to
provide eddy-current damping. The coil is free
Figure 20.6 Campbell bridge. to move in the gap between the soft iron pole