Page 357 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 357
L1644_C08.fm Page 321 Tuesday, October 21, 2003 3:03 PM
MULTIMEDIA
TRANSPORT
CURRENT USEPA RANGS
AIR METHOD
P
L
A INHALED
N SURFACE SURFACE INHALATION
SOIL WATER AIR
T
S SEDIMENT
ROOT ZONE
TAP
WATER DAILY
VADOSE ZONE
INGESTION RISK
DOSE
FOOD
GROUNDWATER ZONE DERMAL
SOIL
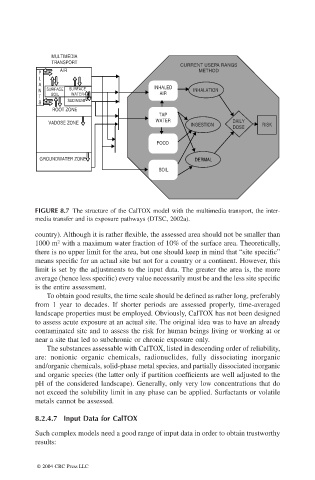
FIGURE 8.7 The structure of the CalTOX model with the multimedia transport, the inter-
media transfer and its exposure pathways (DTSC, 2002a).
country). Although it is rather flexible, the assessed area should not be smaller than
2
1000 m with a maximum water fraction of 10% of the surface area. Theoretically,
there is no upper limit for the area, but one should keep in mind that “site specific”
means specific for an actual site but not for a country or a continent. However, this
limit is set by the adjustments to the input data. The greater the area is, the more
average (hence less specific) every value necessarily must be and the less site specific
is the entire assessment.
To obtain good results, the time scale should be defined as rather long, preferably
from 1 year to decades. If shorter periods are assessed properly, time-averaged
landscape properties must be employed. Obviously, CalTOX has not been designed
to assess acute exposure at an actual site. The original idea was to have an already
contaminated site and to assess the risk for human beings living or working at or
near a site that led to subchronic or chronic exposure only.
The substances assessable with CalTOX, listed in descending order of reliability,
are: nonionic organic chemicals, radionuclides, fully dissociating inorganic
and/organic chemicals, solid-phase metal species, and partially dissociated inorganic
and organic species (the latter only if partition coefficients are well adjusted to the
pH of the considered landscape). Generally, only very low concentrations that do
not exceed the solubility limit in any phase can be applied. Surfactants or volatile
metals cannot be assessed.
8.2.4.7 Input Data for CalTOX
Such complex models need a good range of input data in order to obtain trustworthy
results:
© 2004 CRC Press LLC