Page 275 - Intelligent Digital Oil And Gas Fields
P. 275
Integrated Asset Management and Optimization Workflows 225
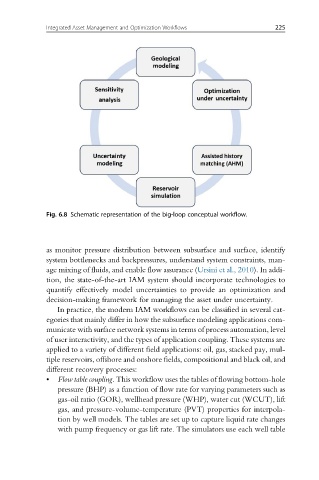
Fig. 6.8 Schematic representation of the big-loop conceptual workflow.
as monitor pressure distribution between subsurface and surface, identify
system bottlenecks and backpressures, understand system constraints, man-
age mixing of fluids, and enable flow assurance (Ursini et al., 2010). In addi-
tion, the state-of-the-art IAM system should incorporate technologies to
quantify effectively model uncertainties to provide an optimization and
decision-making framework for managing the asset under uncertainty.
In practice, the modern IAM workflows can be classified in several cat-
egories that mainly differ in how the subsurface modeling applications com-
municate with surface network systems in terms of process automation, level
of user interactivity, and the types of application coupling. These systems are
applied to a variety of different field applications: oil, gas, stacked pay, mul-
tiple reservoirs, offshore and onshore fields, compositional and black oil, and
different recovery processes:
• Flow table coupling. This workflow uses the tables of flowing bottom-hole
pressure (BHP) as a function of flow rate for varying parameters such as
gas-oil ratio (GOR), wellhead pressure (WHP), water cut (WCUT), lift
gas, and pressure-volume-temperature (PVT) properties for interpola-
tion by well models. The tables are set up to capture liquid rate changes
with pump frequency or gas lift rate. The simulators use each well table