Page 78 - Intelligent Digital Oil And Gas Fields
P. 78
Instrumentation and Measurement 49
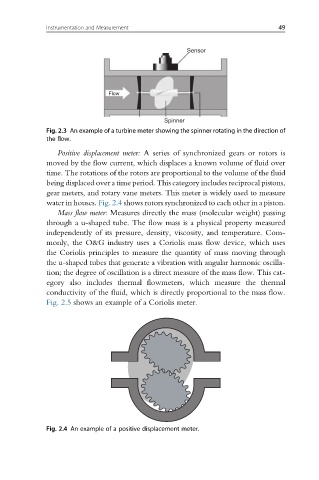
Sensor
Flow
Spinner
Fig. 2.3 An example of a turbine meter showing the spinner rotating in the direction of
the flow.
Positive displacement meter: A series of synchronized gears or rotors is
moved by the flow current, which displaces a known volume of fluid over
time. The rotations of the rotors are proportional to the volume of the fluid
being displaced over a time period. This category includes reciprocal pistons,
gear meters, and rotary vane meters. This meter is widely used to measure
water in houses. Fig. 2.4 shows rotors synchronized to each other in a piston.
Mass flow meter: Measures directly the mass (molecular weight) passing
through a u-shaped tube. The flow mass is a physical property measured
independently of its pressure, density, viscosity, and temperature. Com-
monly, the O&G industry uses a Coriolis mass flow device, which uses
the Coriolis principles to measure the quantity of mass moving through
the u-shaped tubes that generate a vibration with angular harmonic oscilla-
tion; the degree of oscillation is a direct measure of the mass flow. This cat-
egory also includes thermal flowmeters, which measure the thermal
conductivity of the fluid, which is directly proportional to the mass flow.
Fig. 2.5 shows an example of a Coriolis meter.
Fig. 2.4 An example of a positive displacement meter.